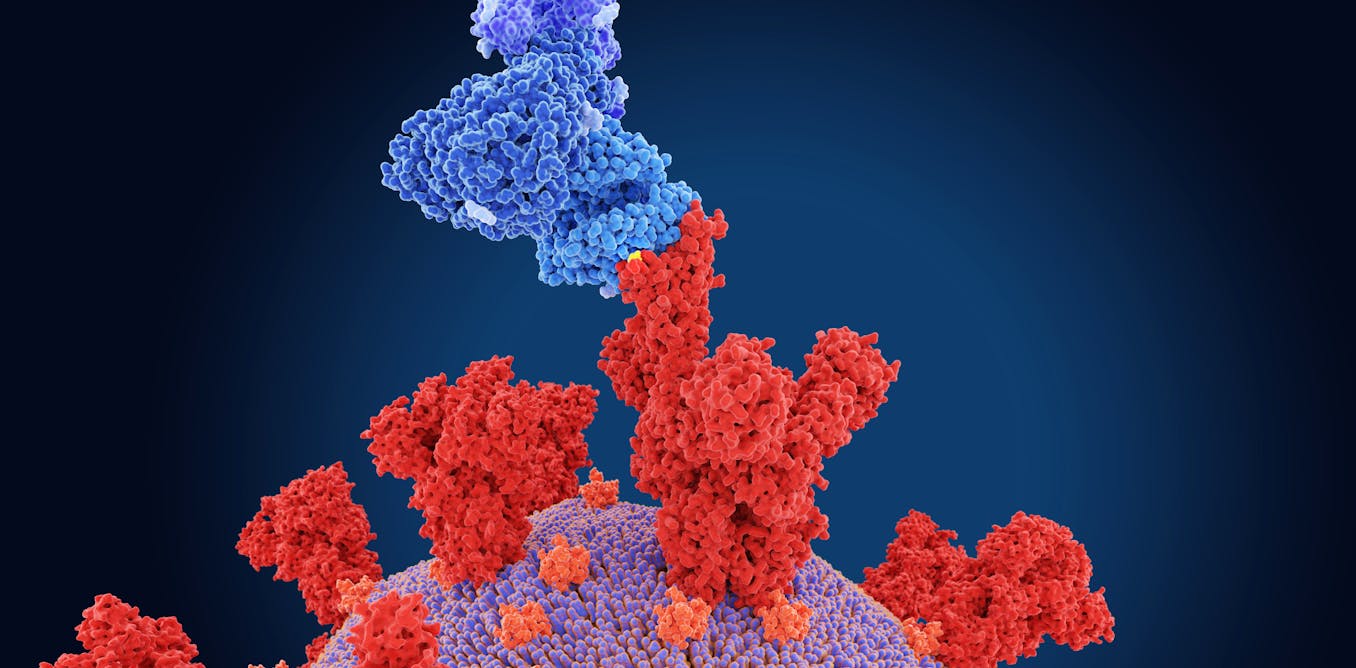
Will omicron – the new coronavirus variant of concern – be more contagious than delta? A virus expert explains what researchers know and what they don't
It’s too early to say whether the newly identified omicron variant is going to overtake delta. But particular mutations in the new strain have researchers deeply concerned.
Nov. 30, 2021 • ~8 min