2018_Southern_Syria_offensive
The 2018 Southern Syria offensive, code-named Operation Basalt (Arabic: عملية البازلت), was a military operation launched by the Syrian Arab Army (SAA) and its allies against the rebels and ISIL in Southern Syria. The fighting began with a surprise attack on rebel-held areas in the eastern part of the Daraa Governorate in an attempt to fracture rebel-held lines and weaken morale, ahead of their offensive in the greater Southern Syria region.[53]
| 2018 Southern Syria offensive | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Daraa Governorate campaign and the Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War | ||||||||
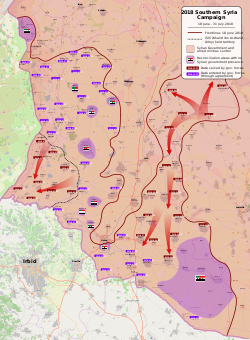 Map of the operation Syrian Army control
Syrian Opposition control
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant control
Reconciliation areas with no Syrian government presence | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
|
Allied militias: |
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||
|
(Tiger Forces) (42nd Armoured Brigade) |
(Criterion Brigades) (Army of Free Tribes) |
| ||||||
| Units involved | ||||||||
|
| |||||||
| Strength | ||||||||
| 40,000[44] |
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
| 309 killed[48][26][49] | 205 killed[48][50] |
310 killed,[26][50][49] 150–200 captured[51][52] | ||||||
| 236 civilians killed[48][49] | ||||||||
Daraa city is known as 'the cradle of the revolution',[54] as the torture and murder of youths from Daraa had been one of the defining events that led to a growth of the protest movement against the Assad government in 2011.[55][56] Thus, analysts have said that its capture by the government would be a key symbolic victory over the rebels, as well as consolidate the government's power in the south of Syria.[57] An estimated 750,000 civilians lived in the region prior to the outbreak of fighting, according to the United Nations (UN).[58]
The offensive was launched in one of the de-escalation (safe) zones agreed upon by Russia, Turkey, and Iran in May 2017.[59] In July that year, the U.S., Russia, and Jordan announced an agreement they had reached for a cease-fire in the areas of Daraa, Quneitra and Sweida.[60][61] Washington then reportedly promised a robust response to any campaign that violated the agreement. However, US forces took no action to stop the assault.[62]
To ease Israeli concerns and prevent possible Israeli intervention, Russia and Israel reached an agreement prior to the offensive that Iranian-backed forces would not aid the Syrian government with the attack on Daraa,[63] and the US government warned rebel forces that they could not expect military support.[64]
Capture of al-Lajat
On 18 June, during the night, the Syrian Army captured several farms near Busra Al-Harir and Masekah. Government forces also attacked the rebel-held towns of Busra Al-Sham, Eastern Ghariyah, and Western Ghariyah. The attacks were focused on rebel fortifications inside the towns. It was also reported that the first phase of the government's offensive in Daraa would focus on Eastern Daraa and capturing the Nasib Border Crossing. While the Syrian Army launched their attacks, rebel forces attempted to push back against the offensive by pushing into the Suwayda Governorate but they were repelled.[65]
On 19 June, the rebels shelled the city of As-Suwayda in response to the government's attacks on their positions, while the Syrian Army simultaneously had another offensive active against ISIL in the northeastern part of the Suwayda Governorate.[66][67][68] Meanwhile, the Syrian Army shelled half a dozen villages outside Daraa city.[69]
Early in the morning on 20 June, the Syrian Army, led by the Tiger Forces, began using heavy artillery and missiles to attempt to take the town of Busra Al-Harir, after capturing a nearby air defense base.[70] Later on the same day, government troops reportedly captured two villages and cut-off the rebel-held al-Lajat region,[71] although the rebels denied this.[72] Subsequently, the Syrian Army's artillery struck many villages.[73]
On 21 June, during the middle of the night, the Syrian Air Force conducted an air raid in the area specifically targeting an Ahrar al-Sham base near Al-Hirak killing 10 fighters from the group. The air raid also targeted almost half a dozen other towns and villages. Along with aerial bombardment, the military also used surface-to-surface missiles and artillery on the villages. The Syrian Army also reportedly cut off rebel supply lines in the area.[74] With government forces firing missiles into rebel-held areas and making excessive gains, the rebels fired missiles into Suwayda in retaliation to the government's offensive.[75]
On 22 June, because of the increased fighting along the Jordan–Syria border, the Jordanian Army was deployed across Jordan's northern border with Syria.[76] Pro-opposition sources reported that government forces had dropped 12 barrel bombs on Busra al-Harir and surrounding towns,[77] while pro-government sources reported that the Syrian Army fired 30 missiles into Busra Al-Sham, Busra Al-Harir, and Al-Karak.[78] On 23 June, after losing five towns, the rebels attacked government-held positions in Daraa itself. The attack included the use of missiles.[79]
On 24 June, Russian military jets provided air cover for the offensive for the first time;[6] the Syrian Network for Human Rights and the Union of Medical Care and Relief Organisations reported pro-government strikes on a medical facility in Busra al-Harir.[80][81] Pro-government sources reported that rebel forces managed to infiltrate government-held checkpoints inside the Suwayda Governorate, but were later repelled.[82] On the next day, the Syrian Army captured 400 km2 of territory, including the whole of the al-Lajat area.[83]
Rapid government gains
On 26 June, the Syrian Army took control of Busra al-Harir after the Tiger Forces attacked the town on multiple axes and broke through rebel lines defending the city. During the clashes, a Syrian Brigadier General was killed.[84][85] Later in the morning of the same day, Syrian Government forces captured two other towns, with rebel fighters withdrawing to Al-Hirak.[86] A rebel counter-attack during the night of 26 June partially reversed the Syrian Army's gains; however, by the early hours of 27 June, the Syrian Army had fully re-established control, pushing forward to capture three more villages and thus reaching the eastern outskirts of Al-Hirak.[87] By this point, the World Food Programme reported that close to 50,000 people had fled their homes in northern Daraa in a week to escape bombs, sheltering in makeshift camps in the south of the governorate and in Quneitra governorate.[88]
27–28 June saw particularly heavy civilian casualties, with the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR) recording 46 dead in two days in the shelling of Bosra al-Sham and other towns.[89] On 27 June, the SAA seized the Brigade 52 Base, as well as a village south of it. Later in the day, government sources said eight locations were deserted or surrendered by rebel forces in sequence, including Al-Hirak and two bases,[90][91][92] although the SOHR said that fighting continued in Al-Hirak.[89] Two days later, government sources reported that some rebel groups and leaders in the southern part of the Daraa province in towns such as Tafas, Da'el, Ibta, Al-Karak, Al-Jay'lah, east of Daraa city agreed to surrender to the Syrian government.[93][94] The Syrian Army also reportedly captured three other locations from rebel factions.[93][94][95]
On 30 June, pro-rebel sources reported that as a result of shelling by pro-government forces the Roman Theatre at Bosra suffered significant damage, having already been hit by Russian airstrikes on 28 June.[96] Between 30 June and 1 July, the Army took control of 13 rebel-held towns, including Bosra al-Sham, after surrender agreements were reached with rebel forces in the area.[97] This extended the government's control to some 60 percent of the province.[98][99] By this time, the UN estimated the number of internally displaced civilians at over 160,000[100] and the Syrian Network for Human Rights reported that over 214 civilians had been killed, including 65 children and 43 women, and that the government and its allies had used 258 surface-to-surface rockets, 293 artillery shells, and at least 397 barrel bombs in the first 15 days of the offensive.[101]
Push towards the Jordanian border
Between 1 and 4 July, the Syrian Army made three unsuccessful attempts to push towards the Nasib Border Crossing, each time being repelled by the rebels. During the fighting, pro-government sources reported that the Army did not have much Russian air support due to the ongoing Russian negotiations with the rebels.[102] However, Syrian warplanes reportedly bombarded Tafas on 1 July, as Republican Guard and Liwa Abu al-Fadl al-Abbas fighters advanced on the ground towards it.[15]
On 2 July, the UN estimated that 270,000 civilians were displaced by the fighting, including 70,000 seeking shelter on the Jordanian border but blocked from entering the country. The civilian half of the opposition's delegation to peace talks withdrew from talks with the government and Russia.[97] The next day, while the offensive was halted, an explosion occurred at a warehouse used by Hezbollah and other Iranian-backed militias in the northern part of the Daraa Governorate along a road between Damascus and Daraa. Several media outlets accused the IDF of carrying out an attack on the facility, but no comment was made by the Israeli Government, and the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights was also unable to verify the cause of the explosion.[103][104] By 4 July, humanitarian agencies said eight hospitals had been bombed since the offensive began, with six medical workers killed, and in total more than 210 civilians killed and 500 injured.[105] Meanwhile, the ISIL-affiliated Khalid ibn al-Walid Army launched an attack against pro-government forces in the village of Sheikh Maskin resulting in the death of several National Defense Force militiamen.[106]
On 3 July, after the failure of previous rounds, negotiations re-opened with Jordanian mediation between Russia and rebel factions.[99]
The following day, the Syrian Army captured the town of Saida, bringing them about six kilometers from the Nasib Border Crossing. The advance came after about 600 airstrikes were conducted in the province[107] over the previous 15 hours.[108] Eventually, the bombardment lasted a total of 22 hours, within which 870 airstrikes and 1,400 rocket and artillery strikes were conducted.[109] Later in the day, the Army captured half a dozen other towns and five border points after launching an attack south of Busra Al-Sham. The advance cleared 230 square kilometers of territory along the border[110] and brought back government troops on the Jordanian frontier for the first time since 2015.[111] That night, between 5 and 6 July, the Syrian Army also seized Al-Naimah, the last town east of Daraa city.[112][113][114]
On 6 July, the Syrian Army was closing in on Nasib, coming within three kilometers of the border crossing.[111] The Army was advancing towards the crossing on two axes, squeezing rebel forces. A military source predicted that the crossing might "fall within a few hours".[115] Soon after, the crossing was seized[116] and the following day soldiers celebrated the capture as troops fanned out across towns and villages in the area.[117] With control being established over the Damascus-Amman highway, the Syrian Army started setting up checkpoints and removing roadblocks along the highway.[118]
On 7 July, Syrian official state media and rebels reported that a ceasefire had been signed by rebel groups to hand over weapons, and that those who rejected the agreement would be transported to Idlib.[119]
Encircling and capture of Daraa city
On 8 July, the Syrian Army began mustering troops for the capture of Daraa city.[120] With several rebel groups surrendering to the government, 11 rebel groups formed the Army of the South to continue fighting the Syrian government and their allies in the south. The group rejected surrendering to the government and vowed to continue fighting for the opposition's cause. The Russian and Syrian air forces conducted 72 airstrikes starting at dawn.[121] The strikes were reportedly conducted after rebels fired on a military convoy on the highway, near Um al-Mayazeen. The Syrian Army then started an assault on Um al-Mayazeen. The fighting postponed the rebels' evacuation.[122]
In an interview with a representative of the Syrian Army Tiger Forces' Taha Regiment conducted by regional expert Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi, the representative described the offensive as intense as the rebels were well-fortified and well-armed. He also stated that many villages captured by the government had rejected Russian-backed reconciliation agreements and that the village of Jabib betrayed a cease-fire agreement, leading to the death of several soldiers in the village. The representative also confirmed that Russia's involvement and support in the offensive was essential to the government's offensive, even more so than Iran's involvement.[123]
On 10 July, it was reported that around 4,000 people fled towards Israeli-controlled territory from the pocket of the province held by ISIL-affiliated Khalid ibn al-Walid Army, expecting a government assault.[124] Later that day, ISIL carried out an SVBIED attack on government forces in the village of Zayzun in western Daraa, claiming that the attack killed more than 35 pro-government fighters. However, pro-opposition activists reported the death toll to be 14 and that it also included recently reconciled rebels.[26][125]
On 11 July, pro-government media reported that the Syrian Air Force provided air support to the FSA in clashes against Khalid ibn al-Walid Army in the town of Hayt in the Yarmouk Basin,[126] and opposition sources reported that Russian planes and government helicopters targeted Khalid ibn al-Walid Army-held Saham al-Golan, the latter dropping barrel bombs.[26] The next day, the ISIL affiliate took control of Hayt from the FSA.[50][127][128] Meanwhile, the government reported a deal had been concluded for rebels to hand over southern Daraa City to government forces; Russian military police and government officers entered the city with journalists to raise the government flag, although rebel fighters remained in the city.[129][50][130]
By this time in the offensive, the government had captured 84% of the territory in the Daraa Governorate, and since the surrender agreements between the government and rebel forces, reports had emerged of pro-government militiamen looting property and stealing from locals in reconciled towns - with Russian military police ignoring and turning a blind eye to it.[131]
Push into Quneitra and rebel surrender
On 15 July, the Syrian Army bombarded Tahrir al-Sham positions in western Daraa, and the Army's Tiger Forces attempted to attack Tahrir al-Sham positions but were repelled. According to government sources, Tahrir al-Sham refused to surrender the area, while the Syrian government stated they were not willing to allow Tahrir al-Sham fighters to reconcile like other rebel groups in the area, but they were offering to deport their fighters to northern Syria. However, Tahrir al-Sham refused this offer and continued to fight.[132] The Syrian Air Force also targeted the rebel-held towns of Al-Harrah and Kafr Nasij in the northwestern part of the Daraa province.[133][134] According to the Syrian Army, they called on the FSA and residents of the town of Al-Harra and its corresponding hilltop, which they considered a strategic point, to expel HTS from the area; HTS also arrested and killed several opposition members that had surrendered to the government, as well as those whom were attempting to do so.[134] On the same day, the first round of rebels and their families (around 400-500 individuals) to be deported to northern Syria departed from Daraa city.[135][136][137][138][139] By this point, Reuters, the World Health Organization and UNICEF reported the government controlled 80% of Daraa province, and that over 160,000 residents displaced by the offensive on Daraa were trapped in Quneitra.[135][140][141]
Syrian Army troops pushed into Quneitra Governorate that day, with the Russian and Syrian air forces conducting over 25 airstrikes on the village of Masahara, 11 km from the Golan frontier.[135][142] Syrian Army and Iranian forces reportedly fired over 800 rockets into rebel-held areas in the Quneitra Governorate,[143][136] and they also targeted a rebel supply line between Daraa and Quneitra.[134] The Syrian Army along with the National Defense Forces paramilitary group attacked the village of Masharah along the border with the Golan Heights, which they said was controlled by Tahrir al-Sham and its allies, and captured the village.[144][133] However, a rebel official in Quneitra denied government forces had captured the village and said fighting continued.[142][145]
On 16 July, the Syrian Army continued shelling western Daraa, with the SOHR estimating that 230 shells hit the area, adding that barrel bombs had been deployed as well.[146] On the same day, the Syrian Army captured the towns of Al-Harra, Al-Nimr, five villages and several hills including the strategic hilltop of Tell al-Harra. After those advances the Syrian Army expanded their control to about 90% of Daraa Province.[147][148][149][150][151][152]
On 17 July, Syrian Army shelling led to significant casualties across the area.[139] Opposition sources and the UN reported that a Syrian Air Force jet targeted Ain al-Tana town in Quneitra, striking a school building sheltering displaced persons, killing six civilians including three children and injuring several others.[150][139] The UN and the NGO Action on Armed Violence also reported Syrian Air Force bombing of Nawa town and surrounding villages that left at least 14 dead and 150 injured, with the World Health Organization reporting that an airstrike hit and damaged Nawa's hospital, one of the only functioning health facilities in the area.[153][139][154] An FSA commander told pro-opposition media that rebels continued to repel the pro-government attack on Mashara.[150] On 18 July, Reporters Without Borders called on the UN to protect reporters at risk due to pro-government advances in the area, reporting 69 journalists in grave danger in Quneitra and Daraa.[155] From 17 to 19 July, the UN reported government air and ground-based strikes on Tasil, Nawa and Ash Shaykh Sa'd in western Daraa, and on Nabe'a Al Sakher in Quneitra governorate.[139] The number of displaced people fluctuated: the UN reported that following these heightened hostilities in Quneitra, IDP numbers had increased to 203,500 individuals, including 45–80,000 newly displaced by the fighting of 17–19 July, as well as people displaced by fighting in ISIL-controlled Yarmouk valley.[139][154]
On 20 July, rebel fighters in the Quneitra Governorate began departing for Idlib after an evacuation agreement was made with the Syrian government, allowing the Syrian Army and allied forces to take control of multiple villages.[156][157] At about the same time, the plan was being finalized for evacuating several hundred members of the civil defense group known as the White Helmets from areas near the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights and into Jordan.[158] The operation was carried out by the Israeli Defense Forces on 22 July 2018; however some 300 White Helmets failed to be evacuated as they were trapped by intense fighting between the Syrian Army and ISIL.[159][160]
Assault on the ISIL pocket
On 21 July 2018, the Syrian Army began their assault on the ISIL-held pocket in the southwest Daraa Province, capturing the Tell al-Jumou hilltop to the southwest of Nawa, and also advancing near the town of Jallin, capturing Tell Ashtara and other nearby areas.[161] ISIL claimed to have killed 25 fighters from the Syrian Army and Syrian opposition in the clashes, and also claimed to capture some villages.[162] Early on the next day, the Syrian army advanced into the village of Jallin.[163]
On 25 July, a series of suicide bombings and raids were carried out by ISIL, targeting civilians in villages and towns in around Suweida, a mainly Druze area under nominal government control but functionally autonomous, with a death toll of up to 255 reported.[164]
On 26 July, according to the Israeli Defense Forces, a Syrian Su-22 jet was shot down by IDF Patriot missiles after the jet was monitored flying around two kilometres (1.2 miles) into Israel. The pilot, Colonel Umran Mare, was killed and the plane crashed in an area on the Syrian side of the border.[165]
On 31 July, the Syrian Army fully captured the remainder of the ISIL-held pocket in the Yarmouk Basin.[3] Around that time, it was reported that 150-200 ISIL militants had surrendered to the Syrian Army.[51][52] After the surrender of ISIL forces on July 31, there were reports that former Daraa FSA fighters who reconciled with the Syrian government and joined the Syrian Army in Yarmouk basin offensive executed dozens of captured fighters of the Khalid Ibn al-Walid army on the same day.[166][167]
- Supranational
 United Nations – The OCHA stated that the UN was "concerned about reports of an escalation of violence in Daraa... which is endangering civilians and causing hundreds of families to become displaced."[168] UN special envoy for Syria Staffan de Mistura warned the offensive by the Syrian Army and Iranian militias would cause a humanitarian disaster and put the lives of over 750,000 people at risk, also stating that more than 45,000 had already been displaced.[169] António Guterres made a statement saying "calls for an immediate halt to the current military escalation and urges all stakeholders to respect their international obligations including the protection of civilians and civilian infrastructure."
United Nations – The OCHA stated that the UN was "concerned about reports of an escalation of violence in Daraa... which is endangering civilians and causing hundreds of families to become displaced."[168] UN special envoy for Syria Staffan de Mistura warned the offensive by the Syrian Army and Iranian militias would cause a humanitarian disaster and put the lives of over 750,000 people at risk, also stating that more than 45,000 had already been displaced.[169] António Guterres made a statement saying "calls for an immediate halt to the current military escalation and urges all stakeholders to respect their international obligations including the protection of civilians and civilian infrastructure." EU – The European Union condemned the violation of the cease-fire zone established in Daraa by the Astana agreement and called on the Syrian Government and their allies to stop the hostilities in Daraa in order to avoid a humanitarian crisis.[170] On 4 July, spokeswoman for the European Union Maja Kocijancic in a written statement said, "Such attacks are clear violations of international law and international humanitarian law that also put at risk any progress in Geneva for the resumption of the political talks under U.N. mediation," and she added, "The renewed violence can also have serious repercussions for the security of neighboring countries, possibly leading to new waves of refugees and internally displaced people."[171]
EU – The European Union condemned the violation of the cease-fire zone established in Daraa by the Astana agreement and called on the Syrian Government and their allies to stop the hostilities in Daraa in order to avoid a humanitarian crisis.[170] On 4 July, spokeswoman for the European Union Maja Kocijancic in a written statement said, "Such attacks are clear violations of international law and international humanitarian law that also put at risk any progress in Geneva for the resumption of the political talks under U.N. mediation," and she added, "The renewed violence can also have serious repercussions for the security of neighboring countries, possibly leading to new waves of refugees and internally displaced people."[171]
- State
 United States – The American Envoy to the UN, Nikki Haley said regarding recent clashes, "The Syrian regime's violations of the ceasefire in southwest Syria need to stop," while also saying, "Russia will ultimately bear responsibility for any further escalations in Syria."[172] After the beginning of the offensive, a letter sent to rebel leadership stated that they "We are fully aware that you have to make your decision according to your interests and the interests of your families and faction as you view them, and you must not base your decision on the assumption or an expectation of a military intervention from our side."[173] The letter also said "We, in the government of the United States of America, understand the hardships that you are facing now, and we are still advising the Russians and the Syrian regime as not to undertake any military action that violates the "de-escalation" agreement in the southwestern part of Syria."[174]
United States – The American Envoy to the UN, Nikki Haley said regarding recent clashes, "The Syrian regime's violations of the ceasefire in southwest Syria need to stop," while also saying, "Russia will ultimately bear responsibility for any further escalations in Syria."[172] After the beginning of the offensive, a letter sent to rebel leadership stated that they "We are fully aware that you have to make your decision according to your interests and the interests of your families and faction as you view them, and you must not base your decision on the assumption or an expectation of a military intervention from our side."[173] The letter also said "We, in the government of the United States of America, understand the hardships that you are facing now, and we are still advising the Russians and the Syrian regime as not to undertake any military action that violates the "de-escalation" agreement in the southwestern part of Syria."[174] Saudi Arabia – Saudi Arabia's permanent delegate to the United Nations Dr. Fahd Al-Mutairi said about the offensive, "Despite urgent appeals and UN resolutions calling for opening of humanitarian corridors and delivering of aid to the needy and affected, the Syrian regime and its allies are continuing their military operations, siege and displacement of innocent civilians in total violation of these resolutions."
Saudi Arabia – Saudi Arabia's permanent delegate to the United Nations Dr. Fahd Al-Mutairi said about the offensive, "Despite urgent appeals and UN resolutions calling for opening of humanitarian corridors and delivering of aid to the needy and affected, the Syrian regime and its allies are continuing their military operations, siege and displacement of innocent civilians in total violation of these resolutions." Vatican – Pope Francis condemned the Syrian military's offensive in Daraa, saying, "the military actions of recent days have struck even schools and hospitals and triggered thousands of new refugees."[175]
Vatican – Pope Francis condemned the Syrian military's offensive in Daraa, saying, "the military actions of recent days have struck even schools and hospitals and triggered thousands of new refugees."[175] Turkey – Turkish foreign minister Mevlüt Çavuşoğlu said the United States, Russia and Iran were responsible for the violations committed by the Syrian Government, the Turkish spokesman for the foreign ministry said regarding the situation, "We strongly condemn these inhuman attacks by the regime on innocent people." He also added, "These attacks hinder the efforts in Astana and (the UN-supported process in) Geneva to reduce violence on the ground and to find a political solution for the crisis,"[176] Turkish officials have stated they are not responsible for upholding agreements made in Daraa but if pro-government forces including Iranian militias and Russian forces attack the Idlib Governorate the Turkish military will uphold the de-escalation agreement and retaliate to violations.[177] Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan told Russian President Vladimir Putin in response to reports emerging of a planned offensive in Idlib after the campaign in Daraa, that the Astana Accord could be completely destroyed, Erdoğan also commented on the targeting of civilians in Daraa.[178]
Turkey – Turkish foreign minister Mevlüt Çavuşoğlu said the United States, Russia and Iran were responsible for the violations committed by the Syrian Government, the Turkish spokesman for the foreign ministry said regarding the situation, "We strongly condemn these inhuman attacks by the regime on innocent people." He also added, "These attacks hinder the efforts in Astana and (the UN-supported process in) Geneva to reduce violence on the ground and to find a political solution for the crisis,"[176] Turkish officials have stated they are not responsible for upholding agreements made in Daraa but if pro-government forces including Iranian militias and Russian forces attack the Idlib Governorate the Turkish military will uphold the de-escalation agreement and retaliate to violations.[177] Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan told Russian President Vladimir Putin in response to reports emerging of a planned offensive in Idlib after the campaign in Daraa, that the Astana Accord could be completely destroyed, Erdoğan also commented on the targeting of civilians in Daraa.[178] Israel – An Israeli defense official stated that the Israeli military will attack any Syrian forces that enter the UN cease-fire zone in the Golan Heights, the official also said about an agreement with the Russian Government, "The agreement is the basis for any future security reality after Assad returns to [Israel's] northern border,"[179] Before departing to meet Russian officials, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said, "Israel has no problem with Assad, but cease-fire agreements must be upheld."[180]
Israel – An Israeli defense official stated that the Israeli military will attack any Syrian forces that enter the UN cease-fire zone in the Golan Heights, the official also said about an agreement with the Russian Government, "The agreement is the basis for any future security reality after Assad returns to [Israel's] northern border,"[179] Before departing to meet Russian officials, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said, "Israel has no problem with Assad, but cease-fire agreements must be upheld."[180] Iran – Hossein Salami, an IRGC commander, said in a speech that there will be the creation of an "Islamic Army" that will end Israel and invade the Golan Heights.[181]
Iran – Hossein Salami, an IRGC commander, said in a speech that there will be the creation of an "Islamic Army" that will end Israel and invade the Golan Heights.[181]
- Domestic
 Tahrir al-Sham – The group released a statement condemning Free Syrian Army groups that made deals with Russia to surrender contested ground in the area; the group also called on all rebel groups in the south to unite and fight as a unified force against the Syrian Government and their allies, and also claimed that they (HTS and their allies) would be victorious.[24][182]
Tahrir al-Sham – The group released a statement condemning Free Syrian Army groups that made deals with Russia to surrender contested ground in the area; the group also called on all rebel groups in the south to unite and fight as a unified force against the Syrian Government and their allies, and also claimed that they (HTS and their allies) would be victorious.[24][182] Guardians of Religion Organization – The organization released a statement regarding the clashes in Daraa, urging Muslims to donate money, and for media platforms to raise awareness to the situation as well as encouraging the opposition factions in Daraa to fight the Syrian military in their advance in the area, the statement also described the importance of defending the region for the rebels saying it's a gateway to the other rebel held areas in the South.[24][183]
Guardians of Religion Organization – The organization released a statement regarding the clashes in Daraa, urging Muslims to donate money, and for media platforms to raise awareness to the situation as well as encouraging the opposition factions in Daraa to fight the Syrian military in their advance in the area, the statement also described the importance of defending the region for the rebels saying it's a gateway to the other rebel held areas in the South.[24][183] Syrian opposition – Various armed opposition groups have condemned the offensive and demanded more international action to halt it. Naser al-Hariri, an opposition negotiator, has condemned the lack of action or intervention by the United States and claimed the only explanation to their lack of action is because of what he described as a malicious deal. In response to the Youth of Sunna Forces surrendering to the Syrian government, by negotiating with Russian officials, two Free Syrian Army Generals condemned the negotiations and described it as treason, stating they were withdrawing from them.[184][185]
Syrian opposition – Various armed opposition groups have condemned the offensive and demanded more international action to halt it. Naser al-Hariri, an opposition negotiator, has condemned the lack of action or intervention by the United States and claimed the only explanation to their lack of action is because of what he described as a malicious deal. In response to the Youth of Sunna Forces surrendering to the Syrian government, by negotiating with Russian officials, two Free Syrian Army Generals condemned the negotiations and described it as treason, stating they were withdrawing from them.[184][185] Caucasus Emirate – The group's branch in Syria released a statement saying the offensive was no different from the one in Eastern Ghouta, and that the offensive is being orchestrated by the Alawite clan of Assad and "Russian Atheists" to wipe out and displace Sunni Muslims in Syria.[186]
Caucasus Emirate – The group's branch in Syria released a statement saying the offensive was no different from the one in Eastern Ghouta, and that the offensive is being orchestrated by the Alawite clan of Assad and "Russian Atheists" to wipe out and displace Sunni Muslims in Syria.[186] Khalid ibn al-Walid Army – A statement from the group said the following about the situation and cooperating with other groups against pro-government forces: "The factions and apostates have been invited to repent and give allegiance to the Islamic State after disavowing their kufr [disbelief] and their loyalty to the disbelievers. There is no truth to the news circulated through rooms and social media pages about Jaysh Khalid bin al-Waleed entering and taking up fronts within the areas of the apostates to fight the Nusayris in them, and in the event an area is entered it will be under the authority of the Caliphate entirely, with no presence for the apostates in them by God's permission. We remind you it is forbidden to contact the apostates except after coordinating with the contact official (Abu Abdo al-Askari) and taking permission in that and within Shari'i regulations, and the one who engages in contact in an individual capacity without coordinating with the contact official will be reprimanded. We ask God Almighty to help us and you to obey Him."[187] The group also published another statement that called on displaced individuals in Southern Syria to migrate to the areas of the Yarmouk Basin under their control.[188]
Khalid ibn al-Walid Army – A statement from the group said the following about the situation and cooperating with other groups against pro-government forces: "The factions and apostates have been invited to repent and give allegiance to the Islamic State after disavowing their kufr [disbelief] and their loyalty to the disbelievers. There is no truth to the news circulated through rooms and social media pages about Jaysh Khalid bin al-Waleed entering and taking up fronts within the areas of the apostates to fight the Nusayris in them, and in the event an area is entered it will be under the authority of the Caliphate entirely, with no presence for the apostates in them by God's permission. We remind you it is forbidden to contact the apostates except after coordinating with the contact official (Abu Abdo al-Askari) and taking permission in that and within Shari'i regulations, and the one who engages in contact in an individual capacity without coordinating with the contact official will be reprimanded. We ask God Almighty to help us and you to obey Him."[187] The group also published another statement that called on displaced individuals in Southern Syria to migrate to the areas of the Yarmouk Basin under their control.[188] Rojava – In the aftermath of the offensive in Southern Syria and talks of a potential operation in the Idlib Governorate officials from Rojava stated they would be willing to cooperate with Russia, Iran, and the Syrian government against opposition and Turkish forces in Idlib they also stated they wished to cooperate with the Syrian government as well as Iran and Russia to retake Afrin.[189][190]
Rojava – In the aftermath of the offensive in Southern Syria and talks of a potential operation in the Idlib Governorate officials from Rojava stated they would be willing to cooperate with Russia, Iran, and the Syrian government against opposition and Turkish forces in Idlib they also stated they wished to cooperate with the Syrian government as well as Iran and Russia to retake Afrin.[189][190]
- Other involved parties
Hezbollah – The Secretary general of Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah, hailed the offensive as a "major victory".[191] In response to pressure put on the group including demands to withdraw from Syria by Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov, Hassan Nasrallah stated that the only way Hezbollah would withdraw from Syria would be if the Syrian Government asked them to leave and said in response to the demands, "I will tell you that if the whole world comes together to force us to leave Syria, they will not be able to evict us."[192]
 Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant – In response to the Syrian government refusing to deport ISIL fighters to the deserts of Eastern Syria, ISIL carried out a large-scale attack in Al-Suwayda, capturing several Druze women and threatened to kill them unless the Syrian government halted the offensive in Daraa.[193]
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant – In response to the Syrian government refusing to deport ISIL fighters to the deserts of Eastern Syria, ISIL carried out a large-scale attack in Al-Suwayda, capturing several Druze women and threatened to kill them unless the Syrian government halted the offensive in Daraa.[193]
By mid-August 2018, Russia set up four Russian military police-manned posts along the Bravo line of the buffer zone in the Golan Heights, with two more planned.[194][195]
In December 2018 SAA forces allegedly seized United States-made weapons in Daraa after local citizens informed the army of weapons caches left behind by the rebels, with Sputnik News releasing footage.[196]
On 1 March 2020, the 2020 Daraa clashes begin.
- "The Latest: Syrian forces drive IS from Golan frontier". AP NEWS. 30 July 2018.
- "Russian jets strike rebel held town in Syria: opposition sources". Reuters. 24 June 2018.
- "Russian jets strike rebel held town in Syria". Jerusalem Post.
- "Russia officially enters southwest Syria offensive despite US warnings". Al-Masdar. 24 June 2018. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army Steps Up Attacks in Southwest, Jordan Concerned". Haaretz. 20 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- Caleb Weiss (27 June 2018). "Confirmed: First evidence of Iranian-controlled militia involvement in southern Syria". Long War Journal. Retrieved 30 June 2018.
- "PLA Fighter Pronounced Dead in Daraa Hostilities". Action Group for Palestinians of Syria. 6 July 2018. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- "Assad regime, Iran prepare for operation in SW Syria". Anadolu Agency.
- Alexandra Gutowski; Caleb Weiss (24 June 2018). "Assad offensive creeps closer to southwest Syria ceasefire zone". Long War Journal. Retrieved 30 June 2018.
- "WATCH: Iranian militia leader appears in video in Daraa". english.alarabiya.net. 2 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- Seth Frantzman IRANIAN-BACKED MILITIA, SYRIA THREATEN TO CUT OFF REBELS NEAR GOLAN, Jerusalem Post, 2 July 2018
- "Military commander in the Southern Front illustrates latest developments of Daraa". 22 June 2018. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "السويداء: "فاطميون" و"النمر" و"حزب الله" لقيادة معركة درعا" [As-Suwayda: Fatimion, Al-Nimr and Hezbollah to lead the battle of Daraa]. Almodon (in Arabic). 26 June 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- "Palestinian Refugee Dies While Fighting alongside Gov't Forces South of Syria". Action Group for Palestinians of Syria. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi (27 July 2018). "The Suwayda' Attacks: Interview". Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- "Rebels suffer worst defeat of war after losing #Daraa to Syrian Army - map". Al-Masdar. 21 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 September 2018. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- Lindsey Snell (30 July 2018). "The Last of the Syrian Good-Guy Rebels". The Daily Beast. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- "Central Operations Room in South hits Syrian regime's armored arsenal of Daraa". Nedaa Syria. 2 July 2018. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- "A Free Army commander warns of upcoming battles in southern Syria". Shaam News Network. 15 June 2018.
- Thomas Joscelyn (27 June 2018). "Jihadists try to rally opposition in southern Syria". Long War Journal. Retrieved 30 June 2018.
- "Assad's Forces Fail to Advance in the Al-Lajat Region in Daraa Governorate". English.enabbaladi.net. 17 May 2018. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- Thomas Joscelyn (11 July 2018). "Islamic State claims suicide attack on Syrian and Russian forces in southern Syria". Long War Journal. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- "SAA's 42nd Brigade redeploys from Golan region to east Daraa". Al-Masdar. 18 June 2018. Archived from the original on 20 June 2018. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- Caleb Weiss (5 July 2018). "Leader of Iranian-backed Shia militia seen inside Syrian military ops room". Long War Journal. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- Al-awsat, Asharq. "Syria: 5 Commanders, 20 Members of Regime Forces Killed East Daraa". aawsat.com.
- Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi (7 July 2018). "The Southern Campaign: Interview with the Tiger Forces' Taha Regiment". Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- "Daraa: Latest Developments Following the Second Round of Negotiations". Enab Baladi. 2 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- "Top ISIL leaders killed in southern Syria". The National. 9 June 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- "ISIS organization never access to new areas in Daraa western suburbs, Jaish Al Thawura says". Nedaa Syria. 2 July 2018. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- Leith Aboufadel (16 July 2018). "Former rebels join Syrian Army's offensive in Daraa". al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- Leith Aboufadel (16 July 2018). "Syrian Army captures town near Israeli-occupied Golan Heights (video)". al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- "The Daraa battle that has no horizon". english.alarabiya.net. 12 July 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "Central military operations room in south of Syria". Syria Call. 20 June 2018. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- "Assad's Forces Attempt Progress towards Tafass City from Three Axes". Enab Baladi. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Rebels in Daraa form new army to fight Syrian forces". Al-Masdar. 8 July 2018. Archived from the original on 21 November 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syrie: 40000 soldats syriens face à 30000 rebelles à Deraa et Quneitra". 22 June 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "Who are the rebels in southern Syria?". AFP. Archived from the original on 30 June 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- "Syrian government retakes Golan Heights frontier with Israel". ABC News. Archived from the original on 30 July 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- Andrew Illingworth. "8,000 to 11,000 ISIS militants still present across Syria – estimates". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 23 November 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
"Over 400 rebels allegedly defect to ISIS in west Daraa". Al-Masdar. 4 July 2018. Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018. - IS-linked group seizes village in south Syria, Al-Araby 12 July 2018
- "Syrian captures more than 200 terrorists alive in largest ISIS mass surrender (video)". Archived from the original on 22 April 2019. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- "Syrian Army attempts to advance in east Daraa before upcoming offensive". Al-Masdar. 19 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- Patrick Wintour Syrian forces' push into east Daraa 'could spark humanitarian crisis', The Guardian, 28 June 2018
- AP Witness: Syrian tortured for not praising Assad, BBS 8 July 2011
- "Witness: Shattered humanity inside Syria's security apparatus". Reuters. 26 May 2011. Archived from the original on 10 July 2018. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- Shelton, Tracey (23 June 2018). "If Daraa falls, could it be the beginning of the end of the Syrian war?". ABC News.
- "Russia, Turkey and Iran continue cooperation on de-escalation zones in Syria". TASS. 23 June 2017.
- "U.S., Russia and Jordan Reach Deal for Cease-Fire in Part of Syria". The New York Times. 7 July 2017.
- "Russia, Jordan agree to speed de-escalation zone in south Syria". Reuters. 11 September 2017.
- The Guardian, 30 June 2018 Syria: southern towns surrender to Assad forces after thousands flee homes
- Ensor, Josie; Sanchez, Raf (29 May 2018). "Russia and Israel 'agree deal' to hold back Iranian militias so Assad can take border region". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022 – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- You're on your own, US tells Syrian rebels, as Assad goes on offensive, Guardian 24 June 2018
- "Syrian military attacks east Daraa ahead of southwest Syria offensive". Al-Masdar. 18 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- agencies, The New Arab & (19 June 2018). "Shells hit Syria's Sweida for first time in three years". Al-Araby.
- "Jihadists carry out first attack on Sweida city in years". Al-Masdar. 19 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- "Syrian regime forces killed 2 civilians in Nahta village in Daraa suburbs, on June 19 – Syrian Network for Human Rights". SOHR. 19 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- "Breaking: Syrian Army launches small offensive in northeast Daraa". Al-Masdar. 20 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army scores first major advance in southwest Syria". Al-Masdar. 20 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- "قوات الأسد تفشل في التقدم بمحيط اللجاة بريف درعا - عنب بلدي". www.enabbaladi.net (in Arabic). Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- "No sleep for rebels in Daraa tonight as Syrian troops launch big assault". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 21 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- "No sleep for rebels in Daraa tonight as Syrian troops launch big assault". Al-Masdar. 21 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- "Jihadi groups launch second attack on Suwayda as battles in northeast Daraa rage". Al-Masdar. 21 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- "Jordanian Army sends large convoy to Syrian border". Al-Masdar. 22 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- Reuters [Syrian barrel bomb attack on rebels jeopardises US-Russia deal] Guardian 23 June 2018
- Czech (22 June 2018). "Syrian Army launches major assault on rebel stronghold in northeast Daraa". Almasdarnews.com. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- Czech (23 June 2018). "Rebels launch retaliatory attack after Syrian Army advances in southwest Syria". Almasdarnews.com. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- Syrian/Russian regime forces bombed makeshift hospital in Busr al Harir town in Daraa suburbs on June 24 Archived 26 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Syrian Network for Human Rights, 25 June 2018
- Syrian military extends southwest assault, thousands displaced, Reuters, 25 June 2018
- "Rebel forces launch fresh attack in southeast Daraa". Al-Masdar. 24 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- "Daraa Map Update: Rebels collapse as Army recaptures Lajat region". Al-Masdar. 26 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- "بعد مئات الضربات الجوية الروسية… قوات النظام والمسلحين الموالين لها تسيطر على بصر الحرير وتربط مناطق سيطرتها في محافظتي درعا والسويداء". 26 June 2018. Retrieved 26 June 2018 – via SOHR.
- "Syrian Army seizes another town in southwest Syria". 26 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2018 – via Al Masdar News.
- "Syrian Army reaches outskirts of rebel stronghold in southwest Syria". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 26 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army captures 54km2 of territory in east Daraa – map". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 27 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- World Food Programme WFP responds to the emergency in southern Syria with cross-border food deliveries for displaced ReliefWeb 26 June 2018
- "Syrian army makes advances in southwest offensive". Channel News Asia. Reuters. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army captures large military base in east Daraa Syrian Army captures large military base in east Daraa". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 28 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- "Rebels abandon several areas in east Daraa as Syrian troops advance". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 28 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army enters 2 rebel settlements in Daraa – SANA". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 28 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- Leith Aboufadel, "Breaking: Syrian Army makes first advance west of Daraa city" Archived 21 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Al Masdar News, 29 June 2018
- "Syrian Army enters another town in east Daraa". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 29 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- "Syrian Army takes control of another town in northern Daraa". AMN – Al-Masdar News | المصدر نيوز. 29 June 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- "Bosra Amphitheater: Syrian World Heritage Site Is Again Target for Shelling". 30 June 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Over 270,000 displaced by south Syria violence, UN says Agence France Presse, 2 July 2018
- "Regime reclaims more ground in south Syria: monitor". France24. 1 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Suha Ma'ayeh Jordan mediating Russia and rebel talks for southern Syria handover, The National, 4 July 2018
- Israel deploys border reinforcements as Syrians flee strikes Guardian 1 July 2018
- Approximately 198,000 Displaced and 214 Killed in South Syria, and the Security Council is Standing Idly By, Syrian Network for Human Rights, 1 July 2018
- "Rebels forestall Syrian Army troops pushing towards Jordanian border". Al-Masdar. 4 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- "Blast reported at Syrian warehouse used by Iranian-backed militias". Times of Israel. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- "Explosions Reported in Syrian, Iranian Weapons Depots in Southern Syria". Ha'aretz. 3 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018 – via Haaretz.
- Fears grow for safety of 270,000 Syrians fleeing fighting in Deraa, Guardian 4 July 2018
- "Breaking: ISIS launches first attack on Syrian Army troops in west Daraa". Al-Masdar. 3 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syria, Russia resume southern offensive after talks collapse". Fox News. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "More than 600 airstrikes target Daraa Province in 15 hours of the return of the hysterical shelling". SOHR. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "About 2300 air and ground strikes target Daraa province in 22 hours of insane shelling and the regime forces expand their control to more than 60% of the province". SOHR. 5 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syrian Army captures 230km2 of territory along Jordanian border – map". Al-Masdar. 6 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "South Syrian rebels agree surrender deal, Assad takes crossing". Today Online. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Breaking: Syrian Army captures last town before Daraa city". Al-Masdar. 6 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- The Guardian 5 July 2018 'Their blankets are the sky': Syrian civilians flee Daraa
- "Daraa Map Update: Syrian Army inching closer to recapture Nassib crossing". Al-Masdar. 6 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syrian Army Takes Jordan Border Crossing From Rebels, State TV Says". Bloomberg.com. 6 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syrian Troops Celebrate Recapture of Jordan Border Crossing". New York Times. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syrian government regains control over Damascus-Amman Highway". Al-Masdar. 7 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- AFP Rebels expected to hand heavy weapons to Assad as south Syria deal said reached, Times of Israel, 7 July 2018
- "Syrian Army prepares for major showdown in Daraa city". Al-Masdar. 8 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Assad regime strikes opposition areas in Syria's Daraa despite truce". Daily Sabah. 8 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syria regime pounds South, rebel evacuations postponed". english.alarabiya.net. 8 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Al-Tamimi, Aymenn Jawad. "The Southern Campaign: Interview with the Tiger Forces' Taha Regiment". Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- AFP Syrians in Islamic State-held area flee toward Israel border, Times of Israel 10 July 2018
- Suicide bomber targets Syrian rebel and regime fighters in Daraa, Al-Arabiya 10 July 2018
- Syrian Air Force helps rebel forces beat back ISIS in west Daraa Archived 16 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Al-Masdar
- Breaking: Rebels handover strategic town to ISIS in west Daraa Archived 16 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Al-Masdar
- Assad's army enters Daraa to take control of the cradle of 2011 uprisings TRT World 12 July 2018
- Assad's forces retake Daraa, birthplace of Syria's uprising, The Guardian 12 July 2018
- "Jihadist rebels make their last stand in west Daraa". Al-Masdar. 15 July 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- Reuters Syrian forces seize village in southwest, widening offensive: monitor Archived 30 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine, UK Business Insider, Jul. 15, 2018
- "Syrian Air Force launches major attack across southwest Syria". Al-Masdar. 15 July 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "Syria: Government troops widen offensive near Quneitra". www.aljazeera.com. Reuters. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "Syrian regime forces close in on area near Israeli-annexed Golan Heights". The National. 15 July 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "First batch of Syrians displaced from Daraa to Idlib". Orient News. Archived from the original on 4 August 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs Syrian Arab Republic: Dar’a, Quneitra, As-Sweida Situation Report No. 3 as of 19 July 2018, ReliefWeb 19 July 2018
- World Health Organization Health Cluster - Syria crisis: Southern Syria Update - Whole of Syria: Issue 6, 13-16 July 2018, ReliefWeb
- UNICEF Access to children in need in Syria continues to be severely restricted, ReliefWeb 19 July 2018
- Russian Warplanes Set Stage for Quneitra Battle, Asharq Al-Awsat, Monday, 16 July 2018
- Hundreds of Assad, Iranian shells fall on Syria’s Quneitra countryside Archived 3 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Orient News, 15 July 2018
- "Breaking: Syrian Army seizes first town in Al-Quneitra". Al-Masdar. 15 July 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- Mashara’da çatışma: Rejim komutanı ve onlarca asker öldürüldü Archived 22 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Asharq Al-Awsat, Monday, 16 July 2018
- "Syrian regime intensifies shelling of 'Triangle of Death' around Daraa". english.alarabiya.net. 16 July 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- Reuters Syrian army says it captures strategic hill overlooking Israeli border, YNet, 16 July 2018
- "Full report from southwest Syria battle - map". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2018.
- Entire Family Killed in Quneitra Governorate, Enab Baladi 17 July 2018
- "Syrian Army captures two more sites in northwest Daraa". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2018.
- "Syrian Army keeps rolling in west Daraa as new areas are captured". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2018.
- Action on Armed Violence Air strikes on Syria’s rebel-held Nawa kills 14 and injures 150, ReliefWeb 19 Jul 2018
- World Health Organization Health Cluster - Syria crisis: Southern Syria Update - Whole of Syria: Issue 7, 17-19 July 2018, ReliefWeb 19 July 2018
- RSF Urges UN to Guarantee Safety of Journalists in South Syria, Asharq Al-Awsat, 18 July 2018
- "Syrian army continues push into Quneitra amid ongoing evacuations". Al Jazeera. 22 July 2018. Retrieved 24 July 2018.
- Musa, Esref; Karacaoglu, Burak (23 July 2018). "3rd convoy of evacuees from Quneitra arrive in Idlib". Anadolu Agency. Retrieved 24 July 2018.
- Allies Prepare to Evacuate White Helmets From Southwest Syria Time, 20 July 2018.
- Syrian 'White Helmets' flee to Jordan with Israeli, Western help Reuters, 22 July 2018.
- 300 White Helmet rescue workers still trapped in Syria CNN, 23 July 2018.
- Zen Adra (21 July 2018). "BREAKING: Syrian Army launches final assault against ISIS in southwest Syria". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- "IS' Hauran Province Claims Killing 25 and Capturing Several Villages in Daraa". 20 July 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- Leith Aboufadel (22 July 2018). "Breaking: Syrian Army scores big advance against ISIS in southwest Syria after Russian air raid". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- Kareem Shaheen Surprise Isis attacks leave more than 200 dead in south-west Syria, The Guardian 25 Jul 2018
- "Israel shoots down Syrian fighter jet in its airspace, military says". The Independent. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- "South Syria: ex-Rebels fighting along government executed 10s of ISIS fighters in Yarmouk Basin. Koayiah,Daraa Governorate". Map of Syrian Civil War - Syria news and incidents today - syria.liveuamap.com.
- "Mass executions carried out by the regime forces and the "reconciliation factions" in Yarmouk basin by killing 34 people and the aerial and ground shelling return as the first round of negotiations with ISIS fails • The Syrian Observatory For Human Rights". Archived from the original on 31 July 2018.
- "Syrian regime intensifies offensive in Daraa province". Trtworld.com. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- Wintour, Patrick (27 June 2018). "Syrian forces' push into east Daraa 'could spark humanitarian crisis'". the Guardian.
- "EU Slams Assad Regime on Syria's Daraa". 4 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Activists: Syrian government steps up offensive in southwest". WTOP. Archived from the original on 23 June 2018. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- Al-Khalidi, Suleiman. "Syrian rebels say U.S. won't intervene in south Syria". U.S. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- "Battle of Southern Syria Has Started". Enab Baladi. 26 June 2018.
- "Pope Francis decries new attacks in Syria's Daraa province". 1 July 2018. Archived from the original on 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Arab, The New (29 June 2018). "Turkey slams Syria regime's 'inhuman' Daraa offensive".
- "Turkish outpost reassurances to Idlib residents about their fate". 11 July 2018. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "If Idlib attacked, Astana accord could be destroyed - Erdogan says". Archived from the original on 25 July 2018. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "Israeli defense official threatens to strike Syrian troops that enter demilitarized zone". 5 July 2018. Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Landau, Noa. "Netanyahu: Israel Has No Problem With Assad, but Cease-fire Agreements Must Be Upheld". Haaretz. Retrieved 18 July 2018.
- "IRGC commander claims 'Islamic Army' near Golan Heights, ready to fight Israel". 10 July 2018. Archived from the original on 11 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 25 June 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Surrender deals in southern Syria a huge gamble". Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Syria's war: Rebel-held Bosra al-Sham surrenders in Deraa battle". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Al-Tamimi, Aymenn Jawad. "Jaysh Khalid bin al-Waleed on Relations With Other Factions: Translation and Analysis". Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Al-Tamimi, Aymenn Jawad. "Jaysh Khalid bin al-Waleed Call for Migration: Translation and Analysis". Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Francis, Ellen (25 July 2018). "Wary of U.S. Ally, Syrian Kurds look to Damascus for talks". Reuters.
- Khoury, Jack (29 June 2018). "Jordanian Official Reports Cease-fire in Southern Syria as Nasrallah Hails 'Very Big Victory'". Haaretz. Reuters.
- "Hezbollah leader says to stay in Syria". Reuters. 8 June 2018.
- "VIDEO: ISIS threatens to slaughter women captives unless Army halts west Daraa offensive". 29 July 2018. Archived from the original on 4 May 2019. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- Russian military police deploys four posts on Golan heights TASS, 14 August 2018.
- На Голанских высотах появились четыре поста российской военной полиции RIA Novosti, 14 August 2018.
- "New video shows Syrian military seizing US-made weapons in Daraa". 21 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 22 December 2018.