Crunode
Crunode
Point where a curve intersects itself at an angle
In mathematics, a crunode (archaic) or node is a point where a curve intersects itself so that both branches of the curve have distinct tangent lines at the point of intersection. A crunode is also known as an ordinary double point.[1]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
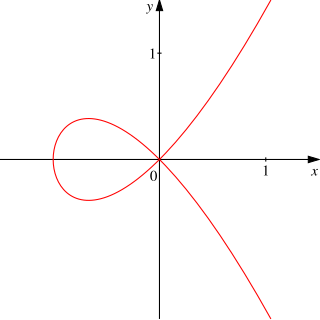
For a plane curve, defined as the locus of points f (x, y) = 0, where f (x, y) is a smooth function of variables x and y ranging over the real numbers, a crunode of the curve is a singularity of the function f, where both partial derivatives and vanish. Further the Hessian matrix of second derivatives will have both positive and negative eigenvalues.


