RestingStateModels.jpg

Size of this preview:
563 × 599 pixels
.
Other resolutions:
226 × 240 pixels
|
451 × 480 pixels
|
796 × 847 pixels
.
Summary
| Description RestingStateModels.jpg |
English:
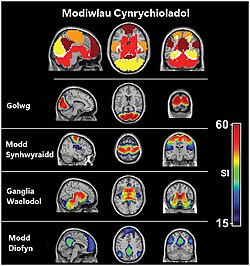
Study showing four functional networks that were found to be highly consistent across subjects. These modules include the visual (yellow), sensory/motor (orange) and basal ganglia (red) cortices as well as the default mode network (precuneus/posterior cingulate, inferior parietal lobes, and medial frontal gyrus; maroon). Overlap among these modules was present but minimal (white).
[1]
|
| Date | |
| Source |
PLoS One. 2012; 7(8): e44428. Published online 2012 August 31 |
| Author | Malaak N. Moussa, Matthew R. Steen, Paul J. Laurienti, and Satoru Hayasaka |
| Other versions |
|
Licensing
This file is licensed under the
Creative Commons
Attribution 2.5 Generic
license.
-
You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
-
Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- ↑ Moussa, Malaak N. ( 2012-08-31 ). "Consistency of Network Modules in Resting-State fMRI Connectome Data". PLoS ONE 7 (8): e44428. Public Library of Science (PLoS). DOI : 10.1371/journal.pone.0044428 . ISSN 1932-6203 .
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
