Geography_of_the_Sahrawi_Arab_Democratic_Republic
Geography of Western Sahara
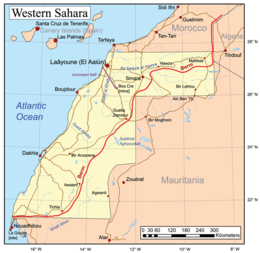
Land features of Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territory in Northern Africa, bordered by the North Atlantic Ocean, Morocco proper, Algeria (Tindouf region), and Mauritania. Geographic coordinates: 24°30′N 13°00′W
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2015) |
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | North Africa |
| Coordinates | 24°30′N 13°00′W |
| Area | Ranked 78th |
| • Total | 266,000 km2 (103,000 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 1,110 km (690 mi) |
| Borders |
|
| Highest point | unnamed elevation: 701 metres (2,300 ft) |
| Lowest point | Sebjet Tah, −55 metres (−180 ft) [citation needed] |



Total: 266,060 square kilometres (102,730 sq mi), about the size of Colorado
- land: 266,000 square kilometres (103,000 sq mi)
- water: 0 square kilometres (0 sq mi)
- Coastline: 1,110 kilometres (690 mi)
- Land boundaries: 2,046 kilometres (1,271 mi) – Algeria: 42 kilometres (26 mi), Mauritania: 1,561 kilometres (970 mi), Morocco: 443 kilometres (275 mi)
- Saguia el-Hamra is the northern third with the city El Aaiún.
- Río de Oro is the southern two-thirds (south of Cape Bojador), with the city Dakhla.
The peninsula in the extreme southwest, with the city of Lagouira, is called Ras Nouadhibou, Cabo Blanco, or Cap Blanc. The eastern side is part of Mauritania.
Maritime claims: contingent upon resolution of sovereignty issue
Terrain
The terrain is mostly low, flat desert with large areas of rocky or sandy surfaces rising to small mountains in south and northeast.
Elevation extremes:
- Lowest point: Sebjet Tah, −55 metres (−180 ft), a depression in the northwest part of Western Sahara straddling the Morocco border
- Highest point: Unnamed elevation, 701 metres (2,300 ft), east of Awsard (Aousserd)[2]
Natural resources
Phosphates, iron ore, and fishing resources on Atlantic Ocean coast
Land use
Arable land: 0.02%
- Permanent crops: 0%
- Other: 99.98% (2005)
Irrigated land: N/A
Natural hazards
Hot, dry, dust/sand-laden sirocco wind can occur during winter and spring; widespread harmattan haze exists 60% of time, often severely restricting visibility. Flash flooding occurs during spring months.
Climate
Western Sahara has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). Annual average rainfall is below 50 millimetres (2.0 in) everywhere. Along the Atlantic coast, averages high and low temperatures are constant and very moderated throughout the year because cool offshore ocean currents considerably cool off the climate, especially during the day. However, summertime is long and extremely hot and wintertime is short and very warm to truly hot further in the interior, where cooling marine influences aren't felt anymore. Average high temperatures exceed 40 °C (104 °F) in summer during a prolonged period of time but can reach as high as 50 °C (122 °F) or even more in places such as Smara, Tichla, Bir Gandus, Bir Anzarane, Aghouinite, Aousserd and others. Average high temperatures exceed 20 °C (68 °F) in winter but average low temperatures can drop to 7 °C (45 °F) in some places. The sky is usually clear and bright throughout the year and sunny weather is the norm.
| Climate data for Laayoune (1981-2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 22.2 (72.0) |
22.7 (72.9) |
24.5 (76.1) |
23.9 (75.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
29.5 (85.1) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.0 (86.0) |
28.6 (83.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
26.2 (79.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.9 (62.4) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
23.3 (73.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 11.6 (52.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
13.9 (57.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
15.8 (60.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.9 (60.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 11.1 (0.44) |
11.1 (0.44) |
5.4 (0.21) |
1.1 (0.04) |
0.5 (0.02) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.5 (0.02) |
1.5 (0.06) |
3.0 (0.12) |
9.8 (0.39) |
13.3 (0.52) |
57.4 (2.26) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 239.1 | 234.7 | 281.4 | 296.5 | 326.5 | 308.9 | 290.3 | 286.9 | 260.1 | 266.1 | 243.9 | 229.8 | 3,264.2 |
| Source: NOAA[3] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Dakhla, Western Sahara | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33.0 (91.4) |
33.9 (93.0) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.2 (99.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
36.0 (96.8) |
38.9 (102.0) |
39.0 (102.2) |
41.8 (107.2) |
39.6 (103.3) |
37.0 (98.6) |
31.6 (88.9) |
42.0 (107.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 20.9 (69.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.5 (79.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.4 (75.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.1 (64.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.8 (69.4) |
18.7 (65.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
13.8 (56.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.9 (58.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
16.7 (62.1) |
17.5 (63.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
16.6 (61.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
16.1 (61.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
11.0 (51.8) |
11.1 (52.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.0 (55.4) |
12.0 (53.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
8.0 (46.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
7.2 (45.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.3 (0.09) |
2.8 (0.11) |
1.0 (0.04) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.4 (0.02) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.4 (0.06) |
2.1 (0.08) |
10.9 (0.43) |
6.3 (0.25) |
2.6 (0.10) |
9.8 (0.39) |
39.7 (1.56) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 10.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 77 | 75 | 75 | 78 | 79 | 81 | 82 | 80 | 77 | 76 | 73 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 254.2 | 245.8 | 275.9 | 276.0 | 306.9 | 291.0 | 266.6 | 272.8 | 249.0 | 254.2 | 240.0 | 241.8 | 3,174.2 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 8.2 | 8.7 | 8.9 | 9.2 | 9.9 | 9.7 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 8.0 | 7.8 | 8.7 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst[4] | |||||||||||||
Current issues
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (May 2022) |
Sparse water and lack of arable land.
This is a list of the extreme points of Western Sahara, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost points – the border with Morocco*
- Easternmost points – the northern section of the border with Mauritania/Algeria**
- Southernmost point – the southern tip of Ras Nouadhibou (Cabo Blanco/Cap Blanc)
- Westernmost point – Cape Dubouchage on Ras Nouadhibou
- Note: Western Sahara does not have a northernmost point, the border being formed by a circle of latitude
- Note: Western Sahara does not have an easternmost point, the border being formed by a meridian
- Western Sahara High Point,Peakbagger.com
- "WMO_Normals_ASCII_60033". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- "Klimatafel von Dakhla (Villa Cisneros) / Westsahara (Dem. Arab. Rep. Sahara)" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 6 November 2018.