Later_Tang
Later Tang
Chinese imperial dynasty from 923 to 937
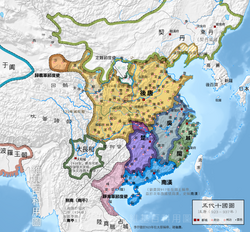
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history.[1]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2008) |
The first three of the Later Tang's four emperors were ethnically Shatuo.[2] The name Tang was used to legitimize itself as the restorer of the Tang dynasty. Although the Later Tang officially began in 923, the dynasty already existed in the years before, as a polity known in historiography as the Former Jin (907–923).
At its height, Later Tang controlled most of northern China.