List_of_regions_in_New_Zealand
Regions of New Zealand
Top administrative divisions of New Zealand
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions (Māori: ngā rohe) for local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils (the top tier of local government), and five are administered by unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities (otherwise the second tier of local government) that also perform the functions of regional councils.[1][2] The Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation.[3]
| Regions | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | |
| Number | 16 |
| Populations | 32,900 (West Coast) – 1,739,300 (Auckland) |
| Areas | 450 km2 (172 sq mi) (Nelson) – 45,350 km2 (17,508 sq mi) (Canterbury) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
History and statutory basis
The regional councils are listed in Part 1 of Schedule 2 of the Local Government Act 2002,[4] along with reference to the Gazette notices that established them in 1989.[5] The Act requires regional councils to promote sustainable development – the social, economic, environmental and cultural well-being of their communities.[6]
The current regions and most of their councils came into being through a local government reform in 1989 that took place under the Local Government Act 1974. The regional councils replaced the more than 700 ad hoc bodies that had been formed in the preceding century – roads boards, catchment boards, drainage boards, pest control boards, harbour boards, domain and reserve boards.[7] In addition they took over some roles that had previously been performed by county councils.
The boundaries of the regions are based largely on drainage basins.[8] This anticipated the responsibilities of the Resource Management Act 1991.[9] Most regional boundaries conform with territorial authority boundaries but there are a number of exceptions. An example is Taupo District, split between four regions, although most of its area is in the Waikato region.[10] There is often a high degree of co-operation between regional and territorial councils as they have complementary roles.
Resource management functions
Regional councils have these specific functions under the Resource Management Act 1991:
- Planning for the integrated management of natural and physical resources[11]
- Planning for regionally significant land uses[12]
- Soil conservation, water quality and quantity, water ecosystems, natural hazards, hazardous substances [13]
- Controlling the coastal marine area[14]
- Controlling via resource consents the taking, use, damming or diverting of water [15]
- Controlling via resource consents the discharge of contaminants[16]
- Establishing of rules in a regional plan to allocate water[17]
- Controlling via resource consents the beds of waterbodies[18]
Other functions
Regional councils have responsibility for functions under other statutes;[19]
- flood and river control under the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Act 1941,
- reserves vested in regional councils under the Reserves Act 1977,
- civil defence under the Civil Defence Act 1990,
- regional pest management under the Biosecurity Act 1993,
- harbour and water navigation under the Maritime Transport Act 1994,
- hazardous waste under the HSNO Act 1996,
- public transport planning under the Land Transport Act 1998, and
- supervision of the safety of dams under the Building Act 2004.[20]
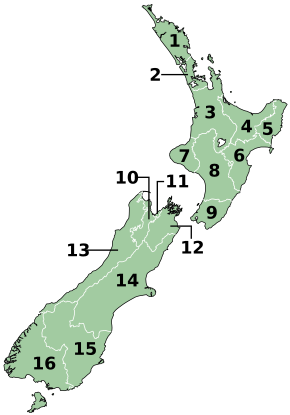
List of regions
| Name (name in Māori if different) |
Regional council | Seats | Council seat | Island | Land area (km2)[21] |
Population[22] | Density
(pop./km2) |
ISO 3166-2 Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northland Te Tai Tokerau |
Northland Regional Council | 9 | Whangārei | North | 12,504 | 203,900 | 16.31 | NZ-NTL |
| 2 | Auckland(1) Tāmaki-makau-rau |
Auckland Council | 21 | Auckland | North | 4,941 | 1,739,300 | 352.01 | NZ-AUK |
| 3 | Waikato | Waikato Regional Council | 14 | Hamilton | North | 23,900 | 522,600 | 21.87 | NZ-WKO |
| 4 | Bay of Plenty Te Moana-a-Toi |
Bay of Plenty Regional Council | 14 | Whakatāne | North | 12,072 | 354,100 | 29.33 | NZ-BOP |
| 5 | Gisborne(1)(2) Te Tairāwhiti |
Gisborne District Council | 14 | Gisborne | North | 8,385 | 52,600 | 6.27 | NZ-GIS |
| 6 | Hawke's Bay Te Matau-a-Māui |
Hawke's Bay Regional Council | 9 | Napier | North | 14,138 | 184,800 | 13.07 | NZ-HKB |
| 7 | Taranaki | Taranaki Regional Council | 11 | Stratford | North | 7,254 | 128,700 | 17.74 | NZ-TKI |
| 8 | Manawatū-Whanganui | Horizons Regional Council | 12 | Palmerston North | North | 22,221 | 260,900 | 11.74 | NZ-MWT |
| 9 | Wellington Te Whanga-nui-a-Tara |
Greater Wellington Regional Council | 13 | Wellington | North | 8,049 | 550,500 | 68.39 | NZ-WGN |
| 10 | Tasman(1) Te Tai-o-Aorere |
Tasman District Council | 13 | Richmond | South | 9,616 | 59,400 | 6.18 | NZ-TAS |
| 11 | Nelson(1) Whakatū |
Nelson City Council | 13 | Nelson | South | 422 | 55,600 | 131.75 | NZ-NSN |
| 12 | Marlborough(1) Te Tauihu-o-te-waka |
Marlborough District Council | 14 | Blenheim | South | 10,458 | 52,200 | 4.97 | NZ-MBH |
| 13 | West Coast Te Tai Poutini |
West Coast Regional Council | 7 | Greymouth | South | 23,245 | 32,900 | 1.42 | NZ-WTC |
| 14 | Canterbury Waitaha |
Environment Canterbury | 14 | Christchurch | South | 44,504 | 666,300 | 14.97 | NZ-CAN |
| 15 | Otago Ōtākou |
Otago Regional Council | 12 | Dunedin | South | 31,186 | 254,600 | 8.16 | NZ-OTA |
| 16 | Southland Murihiku |
Southland Regional Council | 12 | Invercargill | South | 31,196 | 103,900 | 3.33 | NZ-STL |
Notes:
(1) These regions have unitary authorities.
(2) The Gisborne Region is still widely but unofficially known by its former name East Cape or as the East Coast.[23]
Areas outside regional boundaries
Some outlying islands are not included within regional boundaries. The Chatham Islands is not in a region, although its council has some of the powers of a regional council under the Resource Management Act 1991. The Kermadecs and the subantarctic islands are inhabited only by a small number of Department of Conservation staff and there is no regional council for these islands.[24]
Governance
Regional councils are popularly elected every three years in accordance with the Local Electoral Act 2001,[25] except for the Canterbury regional council, which is a mixture of elected councillors and government appointed commissioners.[26] Councils may use a first-past-the-post or single transferable vote system. The chairperson is selected by the elected council members.[27]
Finances
Regional councils are funded through property rates, subsidies from central government, income from trading, and user charges for certain public services. Councils set their own levels of rates, though the mechanism for collecting it usually involves channelling through the territorial authority collection system.[28]
Auckland
The Auckland Regional Council (now the Auckland Council) was preceded by the Auckland Regional Authority (ARA), which existed from 1963 to 1989.[29]
Wellington
The Wellington Regional Council was first formed in 1980 from a merger of the Wellington Regional Planning Authority and the Wellington Regional Water Board.[30]
United councils
In 1978, legislation was passed enabling the formation of regions with united councils. Twenty regions were designated, excluding the Auckland and Wellington areas. For most of the country this was the first regional level of government since the abolition of provinces in 1876. Councillors were not elected directly – they were appointed from the various territorial local authorities (TLAs) within the region.
The only responsibilities mandated by the legislation were coordination of civil defence and development of a regional plan, although the constituent TLAs could agree on additional responsibilities at the point of formation of each united council. For example, in a number of cases the united council took responsibility for the allocation of revenue from regional petrol taxes.
The united councils were based in the facilities of the largest TLA in the region and largely dependent on the TLAs for resources. They were allowed to levy rates but in most cases had minimal operating budgets (below $100,000 per annum). The notable exception was Canterbury, where the united council had a number of responsibilities. Only one united council undertook any direct operational activity – a forestry project in Wanganui.[7]
| Region | United council formed | Levy rates (1982/83) |
|---|---|---|
| Northland | January 1980 | $118,000 |
| Thames Valley | July 1980 | $46,000 |
| Waikato | October 1980 | $36,000 |
| Bay of Plenty | August 1979 | $17,000 |
| Tongariro | November 1979 | $50,000 |
| East Cape | August 1979 | $16,000 |
| Hawke's Bay | December 1983 | – |
| Taranaki | February 1979 | $60,000 |
| Wanganui | May 1979 | $81,000 |
| Wairarapa | November 1978 | $33,000 |
| Manawatu | May 1981 | 0 |
| Horowhenua | June 1980 | $47,000 |
| Nelson Bays | November 1978 | $84,000 |
| Marlborough | December 1978 | $30,000 |
| Canterbury | May 1979 | $605,000 |
| West Coast | November 1978 | $32,000 |
| Aorangi | 1983 | – |
| Coastal / North Otago | April 1983 | – |
| Clutha / Central Otago | November 1980 | $33,000 |
| Southland | May 1979 | $88,000 |
Source: Summary of the Functions and Activities of United Councils. Dept of Internal Affairs, 1984.
- "2013 Census definitions and forms: U". Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Glossary". localcouncils.govt.nz. Department of Internal Affairs. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Chatham Islands Council Act 1995 Archived 12 July 2012 at archive.today, Parliament of New Zealand, 1995, Statute No 041, Commenced: 1 November 1995, retrieved 4 February 2008.
- "Local Government Act 2002 No 84 - Interpretation". Retrieved 17 July 2008.
- "Local Government Act 2002 No 84 - Part 1, Schedule 2". Retrieved 17 July 2008.
- Relationship between the Local Government Act and the RMA Archived 25 March 2006 at the Wayback Machine Quality Planning The RMA Resource, retrieved 11 October 2007.
- Bush, Graham (1995). Local Government & Politics in New Zealand (2nd ed.). Auckland University Press. ISBN 1-86940-126-3.
- OECD Territorial Reviews OECD Territorial Reviews: The Metropolitan Region of Rotterdam-The Hague, Netherlands. OECD Publishing. 2016. p. 169. ISBN 9789264249387.
- New Zealand Historical Atlas – McKinnon, Malcolm (Editor); David Bateman, 1997, Plate 98
- "Property Asset Management Plan 2015-2025" (PDF). Taupo District Council. November 2017. p. 2. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(a)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(b)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(c)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(d)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(e)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(f)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(fa)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991. NB this is a new paragraph added in 2005.
- Resource Management Act, Section 30(1)(g)- Parliament of New Zealand, 1991
- Harris, R. (2004) 'Local government and development legislation', Chapter 3G, Handbook of Environmental Law, Editor Harris, R., ISBN 0-9597851-8-3, Royal Forest and Bird Protection Society of New Zealand, Wellington 2004, p. 130.
- Sections 135, 142, 150, and 154 Building Act 2004, Parliament of New Zealand.
- "Regional Council 2020 Clipped (generalised)". Stats NZ. 30 January 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- "Subnational population estimates (RC, SA2), by age and sex, at 30 June 1996-2023 (2023 boundaries)". Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 25 October 2023. (regional councils); "Subnational population estimates (TA, SA2), by age and sex, at 30 June 1996-2023 (2023 boundaries)". Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 25 October 2023. (territorial authorities); "Subnational population estimates (urban rural), by age and sex, at 30 June 1996-2023 (2023 boundaries)". Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 25 October 2023. (urban areas)
- Soutar, Monty (1 March 2015). "East Coast places - Gisborne". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- "NZ Outlying Islands Regional Information & Travel Information". www.tourism.net.nz. New Zealand Tourism Guide. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Local Government Act 2002, s41(1)(a), Parliament of New Zealand
- Gorman, Paul (30 March 2010). "ECan councillors sacked". The Press. Retrieved 17 August 2010
- Local Government Act 2002, s41(1)(b), Parliament of New Zealand.
- "Local Government (Rating) Act 2002". localcouncils.govt.nz. Department of Internal Affairs. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- "Auckland Regional Authority, 1988". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- Parks Network Plan (PDF). Greater Wellington Regional Council. 2011. p. 10. Retrieved 3 May 2014.