Portal:Energy
Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms. |
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
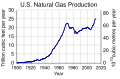
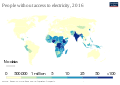
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)

As farmers worldwide respond to higher crop prices in order to maintain the global food supply-and-demand balance, pristine lands are cleared to replace the food crops that were diverted elsewhere to biofuels' production. Because natural lands, such as rainforests and grasslands, store carbon in their soil and biomass as plants grow each year, clearance of wilderness for new farms translates to a net increase in greenhouse gas emissions. Due to this off-site change in the carbon stock of the soil and the biomass, indirect land use change has consequences in the greenhouse gas (GHG) balance of a biofuel. (Full article...)

Photo credit: NASA/TRACE
Plasma being channeled by the magnetic field loops of a sunspot.
- The Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant was the world's first civilian nuclear power plant while Sellafield (pictured) was the world's first commercial nuclear power station?
- The Chinese energy company Fushun Mining Group operates the largest oil shale plant in the world consisting 220 Fushun-type retorts?
- Three of the four largest power stations in the world are in South America?
- Adriatic LNG is the world's first offshore gravity-based structure LNG regasification terminal?
- The Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center is the world's largest wind farm at 735.5 megawatt?
- Scotland has 85% of the United Kingdom's hydro-electric energy resource?
- The day when Exxon canceled its Colony Shale Oil Project in Colorado is known by locals as "Black Sunday"?
- The Australian energy company Linc Energy is the first company in the world to produce synthetic fuel by combining underground coal gasification and gas-to-liquid technologies?
In recognition of Watt's achievements, the SI unit of power, the watt, is named after him.
James Watt was born on 19th of January, 1736 in Greenock, a seaport on the Firth of Clyde. His father was a shipwright, shipowner and contractor, while his mother, Agnes Muirhead, came from a distinguished family and was well-educated. Both were Presbyterians and strong Covenanters. Watt attended school irregularly and instead was mostly schooled at home by his mother.
After studying instrument-making for a year in London, the University of Glasgow offered him the opportunity to set up a small workshop within the university. It was established in 1757. After four years, Watt began to experiment with steam, finally producing a working model steam engine in 1765. Strapped for resources to develop a full-scale engine, Watt was forced to take up employment as a surveyor for eight years. Finally, in 1776, the first engines were installed and working in commercial enterprises.
After further improvements, Watt and foundry owner Matthew Boulton established Boulton and Watt in 1794 to exclusively manufacture steam engines. By 1824 it had produced 1,164 steam engines having a total nominal horsepower of about 26,000.
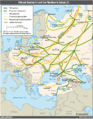
- 7 April 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- The IAEA reports that the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant's Unit 6 was targeted by a drone strike, although nuclear safety has not been compromised, according to the statement. (IAEA)
- 4 April 2024 –
- Researchers at the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument in Arizona, United States, release the largest 3D map of the universe featuring more than six million galaxies. Using this map, researchers are able to measure the acceleration of the expansion rate of the universe with unprecedented accuracy, detecting hints that the rate of expansion has been increasing over time. (The Guardian) (Berkeley Lab)
- "If we already have the Kyoto protocol, why invent another proposal and not just implement one that already exists? If a country is incapable of implementing the result of an international treaty that has established rules and regulations, it won't end up implementing those rules voluntarily."" – Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, 2007
- "Climate change is a challenge China must cope with to realize sustainable development... Implementing a climate change containment policy may cost a fortune, but the cost will be even higher if we delay. Early action is imperative." – Ma Kai, 2007
- "The consequences of restricting the development of developing nations will be much more serious than the consequences of global warming." – Ma Kai, 2007
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
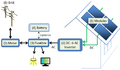
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus