South_African_military_ranks
South African military ranks
List of military ranks
The South African National Defence Force's rank system is largely based on the British system, with the Air Force (and later the Military Health Service) sharing the Army rank titles. Rank titles changed over time as did the insignia.
Army and Air Force ranks
General officers
- Field marshal (1923–c. 1950)
- General (1914– ) (called "commandant-general" 1956–68)
- Lieutenant-general (1914– )
- Major-general (1914– ) (called "combat general" 1960–68)
- Brigadier-general (1912–40, 1998– )
Field officers
- Brigadier (1937–98) (called "colonel-commandant" 1937–40)
- Colonel (1912– )
- Chief commandant (Used in the Commandos 1968–70)[1]
- Lieutenant-colonel (1912– ) (called "commandant" 1950–1988)
Company / junior officers
- Major (1912– )
- Captain (1912– )
- Lieutenant (1912– ) (called "field cornet" 1960–68)
- Second lieutenant (1918– ) (called "assistant field cornet" 1960–68)
Warrant officers
In June 2008[2] a new series of warrant officer ranks were introduced.
- Warrant officer 1st class (1921– )
- Warrant officer 2nd class (1921– )
- Warrant officer (1912–21)
Non-commissioned officers
- Staff sergeant (1912– ) (Air Force equivalent "flight sergeant")
- Sergeant (1912– ) (Air Force equivalent called "air sergeant" until 1970)
- Corporal (1912– ) (Air Force equivalent called "air corporal" until 1970)
- Lance-corporal (1912– ) (Air Force equivalent called "leading air mechanic" until 1970)
Rank and file
- Private (1912– ) (Air Force equivalent called "air mechanic" 1920–70, "private" 1970–82 and "airman" 1982–)
Naval ranks
Flag officers
- Admiral (1972– )
- Vice-admiral (1965– )
- Rear-admiral (1940– )
- Rear-admiral junior grade (1998– )
Senior officers
- Commodore (1946–98)
- Captain (1941– )
- Commander (1913– )
- Lieutenant-commander (1913– )
Junior officers
- Lieutenant (1913– )
- Sub-lieutenant (1913– )
- Ensign (1913– ) (called "acting sub-lieutenant" until 1965)
- Warrant officer 1st class (1955– )
- Warrant officer 2nd class (1955– )
- Warrant officer (1913–55)
Petty officers
- Chief petty officer (1913– )
- Petty officer (1913– )
- Leading seaman (1913– )
- Able seaman (1913– )
Ratings
- Seaman (1913– )
Officers
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1928–1953) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Field Marshal Veldmaarskalk |
General Generaal |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Lieutenant Colonel Luitenant-Kolonel |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant |
Officer Candidate Kandidaatoffisier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other ranks
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1928–1953) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant Officer Class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Staff Sergeant Stafsersant |
Sergeant Sersant |
Corporal Korporaal |
Lance Corporal Onderkorporaal |
Private Soldaat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
During the apartheid era, the South African Army's rank structure was shared between the Army, Air Force and SAMS with some small differences. In the Air Force a staff sergeant was a flight sergeant for example. The Air Force ranks had a blue background and the NCO stripes were blue. For SAMS the ranks had a maroon background.
Officers
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1961–1994)[3] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Generaal[note 1] |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor[note 2] |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Chief Commandant Hoofkommandant[note 3] |
Commandant Kommandant |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant[note 4] |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant[note 5] |
Officer Candidate Kandidaatoffisier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1961–1994) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Generaal |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Commandant Kommandant |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1961–1994) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Admiral Admiraal |
Vice Admiral Vise-Admiraal |
Rear Admiral Skoutadmiraal |
Commodore Kommodoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Commander Kommandeur |
Lieutenant Commander Luitenant-Kommandeur |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Sub Lieutenant Onderluitenant |
Ensign Vaandrig | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1961–1994) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Generaal |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Commandant Kommandant |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other ranks
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1961–1994)[3] |
 |
 |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sergeant Major of the Army Sersant-Majoor van die Leër |
Warrant officer class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant officer class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Staff sergeant Stafsersant |
Sergeant Sersant |
Corporal Korporaal |
Lance corporal Onderkorporaal |
Private Soldaat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1961–1994) |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sergeant Major of the SA Air Force Sersant-Majoor van die SA Lugmag |
Warrant Officer class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant Officer class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Flight sergeant Vlugsersant |
Sergeant Sersant[note 6] |
Corporal Korporaal[note 7] |
Lance corporal Onderkorporaal[note 8] |
Aircraftman Vliegtuigman[note 9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1961–1994) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Master at Arms of the South African Navy Sersant-Majoor van die SA Vloot |
Warrant Officer Class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant Officer Class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Chief petty officer Eerste Bootsman |
Petty officer Bootsman |
Leading seaman Baasseeman |
Able seaman Bevare Seeman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note: in the artillery and anti-aircraft corps, the corporal and lance-corporal are called "bombardier" (bombardeer) and "lance-bombardier" (onderbombardeer). The private is called a "gunner" in the artillery and anti-aircraft, a "rifleman" in the infantry, a "trooper" in the armoured corps, a "sapper" in the engineers, a "signalman" in the signals corps, and a "scout" in the intelligence corps.
Substantive warrant officer posts
Any warrant officer class 1 could be posted to substantive posts, including
- Regimental sergeant major
- Command sergeant major
- Brigade sergeant major
- Sergeant Major of the Army
- Sergeant Major of the Air Force
However they would retain the rank of WO1, while wearing unique rank insignia. To distinguish the posting different colour backgrounds were used; for example, red for regimental sergeant major and black for command sergeant major. The sergeant major of each arm of service wore insignia topped by the arms of their respective arm of service.
In 2008 the warrant officer ranks were expanded to make each substantive rank a formal rank.
The SA Army was formed in 1912 as the Union Defence Force. It was given its present name in 1951. The rank system is derived from that of the British Army.
The ranks of General Officers changed in September 2003 when the rank previously called Brigadier became known as Brigadier General.[4][5]
Officers
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
 |
 |
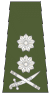 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Generaal |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Commandant Kommandant |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | 2nd lieutenant | Candidate officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrant officers
| Equivalent NATO rank |
WO-5 | WO-4 | WO-3 | WO-2 | WO-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master chief warrant officer | Senior chief warrant officer | Chief warrant officer | Master warrant officer | Senior warrant officer | ||||||
Other ranks
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant officer class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Staff sergeant Stafsersant |
Sergeant Sersant |
Corporal Korporaal |
Lance corporal Onderkorporaal |
Private (or equivalent) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance corporal | Private (or equivalent) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The SA Air Force was formed in 1920. Unlike many other Commonwealth air forces, it had an army style rank system. In 2002 the Air Force officer rank insignia structure was changed from one which was shared with the Army to a new pattern based on stripes. The Air Force stated that this was "in order to bring it more in line with international forms of rank".[8] The army-style rank titles were retained. Note: The rank of General is only used when the Chief of the Air Force is also the Chief of the Defence Force which has occurred on occasion in the past. In 2005 the South African Air Force redesigned its insignia completely, while keeping the Army titles.
Officers
| Rank group | General/Flag/Air officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Generaal |
Lieutenant General Luitenant-Generaal |
Major General Generaal-Majoor |
Brigadier Brigadier |
Colonel Kolonel |
Commandant Kommandant |
Major Majoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Second Lieutenant Tweede Luitenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | Officer candidate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrant officers
| Equivalent NATO rank | WO-5 | WO-4 | WO-3 | WO-2 | WO-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master chief warrant officer | Senior chief warrant officer | Chief warrant officer | Master warrant officer | Senior warrant officer | ||
Other ranks
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant Officer Class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Flight Sergeant Vlugsersant |
Sergeant Sersant |
Corporal Korporaal |
Lance corporal Onderkorporaal |
Aircraftman Vliegtuigman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Flight sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance corporal | Aircraftman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The SA Navy was originally two separate organisations, namely the South African Division of the Royal Navy Volunteer Reserve (formed in 1913) and the South African Naval Service (formed in 1922 and renamed the "Seaward Defence Force" in 1939). They amalgamated in 1942 to form the SA Naval Forces, which were renamed "SA Navy" in 1951. The rank system is based on that of the (British) Royal Navy.[10]
The ranks of flag officers changed in 1997 when the rank previously called Commodore became known as Rear Admiral (Junior Grade).[11]
Officers
| Rank group | General/flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Admiral Admiraal |
Vice Admiral Vise-Admiraal |
Rear Admiral Skoutadmiraal |
Commodore Kommodoor |
Captain Kaptein |
Commander Kommandeur |
Lieutenant Commander Luitenant-Kommandeur |
Lieutenant Luitenant |
Sub Lieutenant Onderluitenant |
Ensign Vaandrig |
Midshipman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
  |
  |
  |
  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Rear admiral (junior grade) |
Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander |
Lieutenant | Sub lieutenant | Ensign | Midshipman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrant Officers
| Equivalent NATO rank | WO-5 | WO-4 | WO-3 | WO-2 | WO-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master chief warrant officer | Senior chief warrant officer | Chief warrant officer | Master warrant officer | Senior warrant officer | ||||||
Enlisted
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1994-2002)[6] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 Adjudant-Offisier Klas I |
Warrant Officer Class 2 Adjudant-Offisier Klas II |
Chief petty officer Eerste Bootsman |
Petty officer Bootsman |
Leading seaman Baasseeman |
Able seaman Bevare Seeman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Chief petty officer | Petty officer | Leading seaman | Able seaman | Seaman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The South African Military Health Service uses the Army rank system. There is a differentiation in that the rank insignia is displayed on a red background as opposed to the Army, which is displayed on an olive background.
Officers
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Military Health Service |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | 2nd lieutenant | Candidate officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enlisted
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Military Health Service |
 |
 |
 |
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 | Warrant Officer Class 2 | Staff Sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Private (or equivalent) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The highest ranking South African non-commissioned officer is the Warrant Officer of the South African National Defence Force. They are the sole holder of the rank of Master Chief Warrant Officer (NATO equivalent WO-5).[13] As of October 2012 the incumbent MCWO is Mothusi Kgaladi[14]
The rank of Senior Chief Warrant Officer (NATO equivalent WO-4) is only held by the Master at Arms of the Navy, the Sergeant Major of the Army, the Sergeant Major of the Air Force, and the Sergeant Major of the Military Health Service.[13]
- Called Commandant general (Kommandant-generaal) from 1956 to 1968
- Called Combat general (Bestry generaal) from 1960 to 1968
- Only in the Commandos from 1968 to 1970
- Called Field cornet (Veldkornet) from 1960 to 1968
- Called Assistant field cornet (Assistent veldkornet) from 1960 to 1968
- Called Air Sergeant (Lugsersant) from 1960 to 1968
- Called Air Corporal (Lugkorporaal) from 1960 to 1968
- Called Leading air mechanic (Leiend Lugwerktuigkundige) until 1970
- Called Air mechanic (Lugwerktuigkundige) from 1920 to 1970
Called Private (Soldaat) from 1970 to 1982
- Radburn, Arthur (1990). "South African Army Ranks and Insignia". South African Journal of Military Studies. 20 (2): 2.
- Pale, Frans (Lt Col). "DOD News Sep 2008" (PDF). SA Department of Defence. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- Radburn, A. (22 February 2012). "SOUTH AFRICAN ARMY RANKS AND INSIGNIA". Scientia Militaria: South African Journal of Military Studies. 20 (2): 1–4. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- "Airforce Rank Structure". Unofficial SA Airforce website.
- "Uniform: rank insignia". army.mil.za. Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2021.
- Smaldone, Joseph P. (1997). "National Security". In Byrnes, Rita M. (ed.). South Africa: a country study. Area Handbook (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. pp. 378–379. LCCN 96048983. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- "Uniform: Rank insignia". army.mil.za. Department of Defence (South Africa). Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- "Rank Insignia". af.mil.za. Department of Defence (South Africa). Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- "Rank insignia of the South African Navy". navy.mil.za. Archived from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2021.
- Bennett, C. H.; Söderlund, A. G. (2008). South Africa's navy : a navy of the people and for the people. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-620-41446-3.
- "Rank Insignia". navy.mil.za. Department of Defence (South Africa). Archived from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- "Mothusi Victor Kgaladi new WO SANDF". DefenceWeb.