Estrone_glucuronide
Estrone glucuronide
Chemical compound
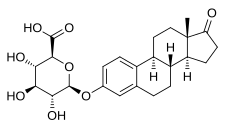
Estrone glucuronide, or estrone-3-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estrone.[1] It is formed from estrone in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys.[1] It has much higher water solubility than does estrone.[1] Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates and estrone glucuronide is the dominant metabolite of estradiol.[1]
When exogenous estradiol is administered orally, it is subject to extensive first-pass metabolism (95%) in the intestines and liver.[2][3] A single administered dose of estradiol is absorbed 15% as estrone, 25% as estrone sulfate, 25% as estradiol glucuronide, and 25% as estrone glucuronide.[2] Formation of estrogen glucuronide conjugates is particularly important with oral estradiol as the percentage of estrogen glucuronide conjugates in circulation is much higher with oral ingestion than with parenteral estradiol.[2] Estrone glucuronide can be reconverted back into estradiol, and a large circulating pool of estrogen glucuronide and sulfate conjugates serves as a long-lasting reservoir of estradiol that effectively extends its terminal half-life of oral estradiol.[2][3] In demonstration of the importance of first-pass metabolism and the estrogen conjugate reservoir in the pharmacokinetics of estradiol,[2] the terminal half-life of oral estradiol is 13 to 20 hours[4] whereas with intravenous injection its terminal half-life is only about 1 to 2 hours.[5]
Metabolic pathways of estradiol in humans
|