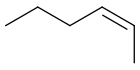
Hexene
Hexene
Organic molecule with the formula C6H12
In organic chemistry, hexene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C6H12. The prefix "hex" is derived from the fact that there are 6 carbon atoms in the molecule, while the "-ene" suffix denotes that there is an alkene present—two carbon atoms are connected via a double bond. There are several isomers of hexene,[1] depending on the position and geometry of the double bond in the chain. One of the most common industrially useful isomers is 1-hexene, an alpha-olefin. Hexene is used as a comonomer in the production of polyethylene.