Radiant_flux
Radiant flux
Measure of radiant energy over time
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt (W), one joule per second (J/s), while that of spectral flux in frequency is the watt per hertz (W/Hz) and that of spectral flux in wavelength is the watt per metre (W/m)—commonly the watt per nanometre (W/nm).
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
Radiant flux
Radiant flux, denoted Φe ('e' for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined as[1]
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\Phi _{\mathrm {e} }&={\frac {dQ_{\mathrm {e} }}{dt}}\\[2pt]Q_{\mathrm {e} }&=\int _{\Sigma }\mathbf {S} \cdot {\hat {\mathbf {n} }}\,dA\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ffd63c88141021c493a1f7676528a47d76f34200)
where
- t is the time;
- Qe is the radiant energy flux of the field out of a closed surface Σ;
- S is the Poynting vector, representing the current density of radiant energy;
- n is the normal vector of a point on Σ;
- A represents the area of Σ.
But the time-average of the norm of the Poynting vector is used instead, because in radiometry it is the only quantity that radiation detectors are able to measure:

where ⟨-⟩ is the time-average, and α is the angle between n and
Spectral flux
Spectral flux in frequency, denoted Φe,ν, is defined as[1]

where ν is the frequency.
Spectral flux in wavelength, denoted Φe,λ, is defined as[1]

where λ is the wavelength.
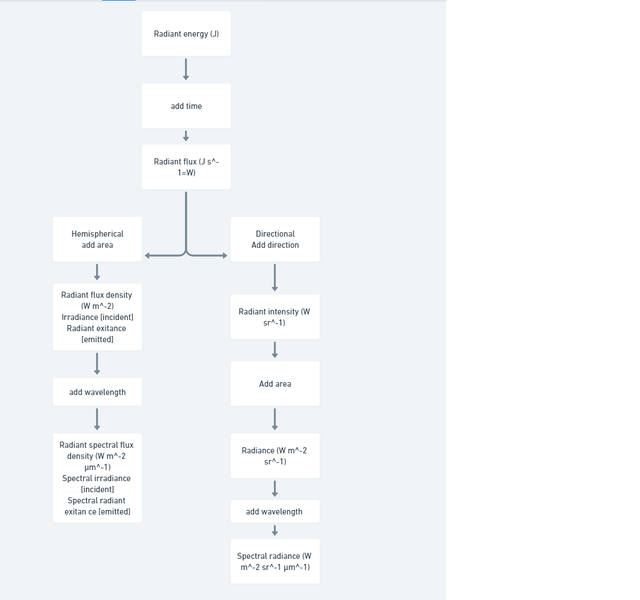
| Quantity | Unit | Dimension | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol[nb 1] | Name | Symbol | ||
| Radiant energy | Qe[nb 2] | joule | J | M⋅L2⋅T−2 | Energy of electromagnetic radiation. |
| Radiant energy density | we | joule per cubic metre | J/m3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−2 | Radiant energy per unit volume. |
| Radiant flux | Φe[nb 2] | watt | W = J/s | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | Radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time. This is sometimes also called "radiant power", and called luminosity in Astronomy. |
| Spectral flux | Φe,ν[nb 3] | watt per hertz | W/Hz | M⋅L2⋅T −2 | Radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅nm−1. |
| Φe,λ[nb 4] | watt per metre | W/m | M⋅L⋅T−3 | ||
| Radiant intensity | Ie,Ω[nb 5] | watt per steradian | W/sr | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | Radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit solid angle. This is a directional quantity. |
| Spectral intensity | Ie,Ω,ν[nb 3] | watt per steradian per hertz | W⋅sr−1⋅Hz−1 | M⋅L2⋅T−2 | Radiant intensity per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅sr−1⋅nm−1. This is a directional quantity. |
| Ie,Ω,λ[nb 4] | watt per steradian per metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−1 | M⋅L⋅T−3 | ||
| Radiance | Le,Ω[nb 5] | watt per steradian per square metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | Radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a surface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area. This is a directional quantity. This is sometimes also confusingly called "intensity". |
| Spectral radiance Specific intensity |
Le,Ω,ν[nb 3] | watt per steradian per square metre per hertz | W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 | M⋅T−2 | Radiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅nm−1. This is a directional quantity. This is sometimes also confusingly called "spectral intensity". |
| Le,Ω,λ[nb 4] | watt per steradian per square metre, per metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−3 | ||
| Irradiance Flux density |
Ee[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W/m2 | M⋅T−3 | Radiant flux received by a surface per unit area. This is sometimes also confusingly called "intensity". |
| Spectral irradiance Spectral flux density |
Ee,ν[nb 3] | watt per square metre per hertz | W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 | M⋅T−2 | Irradiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. This is sometimes also confusingly called "spectral intensity". Non-SI units of spectral flux density include jansky (1 Jy = 10−26 W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1) and solar flux unit (1 sfu = 10−22 W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 = 104 Jy). |
| Ee,λ[nb 4] | watt per square metre, per metre | W/m3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−3 | ||
| Radiosity | Je[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W/m2 | M⋅T−3 | Radiant flux leaving (emitted, reflected and transmitted by) a surface per unit area. This is sometimes also confusingly called "intensity". |
| Spectral radiosity | Je,ν[nb 3] | watt per square metre per hertz | W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 | M⋅T−2 | Radiosity of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅m−2⋅nm−1. This is sometimes also confusingly called "spectral intensity". |
| Je,λ[nb 4] | watt per square metre, per metre | W/m3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−3 | ||
| Radiant exitance | Me[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W/m2 | M⋅T−3 | Radiant flux emitted by a surface per unit area. This is the emitted component of radiosity. "Radiant emittance" is an old term for this quantity. This is sometimes also confusingly called "intensity". |
| Spectral exitance | Me,ν[nb 3] | watt per square metre per hertz | W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 | M⋅T−2 | Radiant exitance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in W⋅m−2⋅nm−1. "Spectral emittance" is an old term for this quantity. This is sometimes also confusingly called "spectral intensity". |
| Me,λ[nb 4] | watt per square metre, per metre | W/m3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−3 | ||
| Radiant exposure | He | joule per square metre | J/m2 | M⋅T−2 | Radiant energy received by a surface per unit area, or equivalently irradiance of a surface integrated over time of irradiation. This is sometimes also called "radiant fluence". |
| Spectral exposure | He,ν[nb 3] | joule per square metre per hertz | J⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 | M⋅T−1 | Radiant exposure of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The latter is commonly measured in J⋅m−2⋅nm−1. This is sometimes also called "spectral fluence". |
| He,λ[nb 4] | joule per square metre, per metre | J/m3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−2 | ||
| See also: | |||||
- Standards organizations recommend that radiometric quantities should be denoted with suffix "e" (for "energetic") to avoid confusion with photometric or photon quantities.
- Alternative symbols sometimes seen: W or E for radiant energy, P or F for radiant flux, I for irradiance, W for radiant exitance.
- Spectral quantities given per unit wavelength are denoted with suffix "λ".
- "Thermal insulation — Heat transfer by radiation — Physical quantities and definitions". ISO 9288:1989. ISO catalogue. 1989. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
- Boyd, Robert (1983). Radiometry and the Detection of Optical Radiation (Pure & Applied Optics Series). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-86188-1.
