STS-7
STS-7
1983 American crewed spaceflight
STS-7 was NASA's seventh Space Shuttle mission, and the second mission for the Space Shuttle Challenger. During the mission, Challenger deployed several satellites into orbit. The shuttle launched from Kennedy Space Center on June 18, 1983, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base on June 24, 1983. STS-7 carried Sally Ride, America's first female astronaut.
Challenger as photographed by the SPAS-1 satellite on June 22, 1983 | |
| Names | Space Transportation System-7 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1983-059A |
| SATCAT no. | 14132 |
| Mission duration | 6 days, 2 hours, 23 minutes, 59 seconds (achieved) |
| Distance travelled | 3,570,000 km (2,220,000 mi) |
| Orbits completed | 97 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Challenger |
| Launch mass | 113,025 kg (249,177 lb) |
| Landing mass | 92,550 kg (204,040 lb) |
| Payload mass | 16,839 kg (37,124 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 5 |
| Members | |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | June 18, 1983, 11:33:00; 40 years ago (June 18, 1983, 11:33:00) |
| Rocket | Space Shuttle Challenger |
| Launch site | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A |
| Contractor | Rockwell International |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | June 24, 1983, 13:56:59 UTC |
| Landing site | Edwards Air Force Base, Runway 15 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 299 km (186 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 307 km (191 mi) |
| Inclination | 28.30° |
| Period | 90.60 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| |
STS-7 mission patch Ride, Fabian, Crippen, Thagard, Hauck | |
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Robert Crippen Second spaceflight | |
| Pilot | Frederick Hauck First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 1 | John M. Fabian First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 2 | Sally Ride First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 3 | Norman Thagard First spaceflight | |
Support crew
- John E. Blaha
- Roy D. Bridges Jr. (ascent CAPCOM)
- Guy Gardner
- Terry Hart
- Jon McBride
- Bryan D. O'Connor (entry CAPCOM)
Crew seat assignments
| Seat[1] | Launch | Landing | 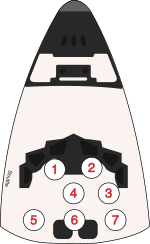 Seats 1–4 are on the Flight Deck. Seats 5–7 are on the Middeck. |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Crippen | Crippen | |
| S2 | Hauck | Hauck | |
| S3 | Fabian | Fabian | |
| S4 | Ride | Ride | |
| S5 | Thagard | Thagard |
STS-7 began on June 18, 1983, with an on-time liftoff at 7:33:00 a.m. EDT. It was the first spaceflight of an American woman (Ride), the largest crew to fly in a single spacecraft up to that time (five people), and the first flight that included members of NASA's Group 8 astronaut class, which had been selected in 1978 to fly the Space Shuttle. President Ronald Reagan also sent his personal favorite Jelly Belly jelly beans with the astronauts, making them the first jelly beans in space. The crew had already ate lunch with the president at the White House on June 1, the first time that a crew did so before launch rather than after.[2]
The crew of STS-7 included Robert Crippen, commander, making his second Shuttle flight; Frederick Hauck, pilot; and Sally Ride, John M. Fabian and Norman Thagard, all mission specialists. Thagard conducted medical tests concerning Space adaptation syndrome, a bout of nausea frequently experienced by astronauts during the early phase of a space flight.
Two communications satellites – Anik C2 for Telesat of Canada, and Palapa B1 for Indonesia – were successfully deployed during the first two days of the mission; both were Hughes-built HS-376-series satellites. The mission also carried the first Shuttle pallet satellite (SPAS-1), which was built by the West German aerospace firm Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB). SPAS-1 was unique in that it was designed to operate in the payload bay or be deployed by the Remote Manipulator System (Canadarm) as a free-flying satellite. It carried 10 experiments to study formation of metal alloys in microgravity, the operation of heat pipes, instruments for remote sensing observations, and a mass spectrometer to identify various gases in the payload bay. It was deployed by the Canadarm and flew alongside and over Challenger for several hours, performing various maneuvers, while a U.S.-supplied camera mounted on SPAS-1 took pictures of the orbiter. The Canadarm later grappled the pallet and returned it to the payload bay.
STS-7 also carried seven Getaway Special (GAS) canisters, which contained a wide variety of experiments, as well as the OSTA-2 payload, a joint U.S.-West Germany scientific pallet payload. Finally, the orbiter's Ku-band antenna was able to relay data through the U.S. tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) to a ground terminal for the first time.
STS-7 was scheduled to make the first orbiter landing at Kennedy Space Center's then-new Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). Unacceptable weather forced a change to Runway 15 at Edwards Air Force Base. The landing took place on June 24, 1983, at 06:56:59 a.m. PDT. The mission lasted 6 days, 2 hours, 23 minutes, and 59 seconds, and covered about 3,570,000 km (2,220,000 mi) during 97 orbits of the Earth. Challenger was returned to KSC on June 29, 1983.
STS-7 experienced the first known Space Shuttle external tank (ET) bipod ramp foam shedding event during launch. This was the root cause of the eventual loss of Columbia during STS-107 almost two decades later. While Challenger was on-orbit, one of its windows was damaged non-critically by space debris.[3]
The seven white stars in the black field of the mission patch, as well as the arm extending from the orbiter in the shape of a 7, indicate the flight's numerical designation in the Space Transportation System's mission sequence. The five-armed symbol on the right side illustrates the four male/one female crew.
NASA began a tradition of playing music to astronauts during the Project Gemini, and first used music to wake up a flight crew during Apollo 15. Each track is specially chosen, often by the astronauts' families, and usually has a special meaning to an individual member of the crew, or is applicable to their daily activities.[4]
| Flight Day | Song | Artist/Composer | Played for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 2 | "Aggie War Hymn"/"University of Texas Fight Song" | Fightin' Texas Aggie Band/University of Texas band | Bob Crippen[lower-alpha 1] |
| Day 3 | "Aggie War Hymn"/"Tufts Tonia's Day" | Fightin' Texas Aggie Band/The Tufts University Beelzebubs | Rick Hauck |
| Day 4 | Medley: "Aggie War Hymn"/"Reveille"/"When You're Smiling" | Fightin' Texas Aggie Band/Unknown/Dr. Howard E. Cleave | Mary L. Cleave[lower-alpha 2] |
| Day 5 | "Washington State University Cougar Fight Song" | Washington State University Band | John Fabian |
| Day 6 | "Stanford Hymn" | Leland Stanford Junior University Marching Band | Sally Ride |
| Day 7 | "Florida State University Fight Song" | Florida State University Marching Chiefs | Norm Thagard |
- The second launch of Challenger
- Deployment of Palapa B1
- Deployment of Anik C2
- Window pit caused by impact of space debris
- SPAS-1 grappled by the Canadarm
- Sherr, Lynn (2014). Sally Ride: America's First Woman in Space. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4767-2578-9. OCLC 885483468.
- "Orbital Debris Photo Gallery". NASA. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved August 12, 2010.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Fries, Colin (June 25, 2007). "Chronology of Wakeup Calls" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 20, 2023. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Graye, Michelle. Houston We Have a Wake-up Call. Lulu.com. ISBN 9781257805525 – via Google Books.
- STS-7 mission summary NASA
- STS-7 video highlights NSS
- Interview with Sally Ride and STS-7 mission footage Texas Archive of the Moving Image