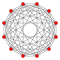
6-cube
6-cube
6-dimensional hypercube
In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 vertices, 192 edges, 240 square faces, 160 cubic cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces.
| 6-cube Hexeract | |
|---|---|
 Orthogonal projection inside Petrie polygon Orange vertices are doubled, and the center yellow has 4 vertices | |
| Type | Regular 6-polytope |
| Family | hypercube |
| Schläfli symbol | {4,34} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| 5-faces | 12 {4,3,3,3} |
| 4-faces | 60 {4,3,3} |
| Cells | 160 {4,3} |
| Faces | 240 {4} |
| Edges | 192 |
| Vertices | 64 |
| Vertex figure | 5-simplex |
| Petrie polygon | dodecagon |
| Coxeter group | B6, [34,4] |
| Dual | 6-orthoplex |
| Properties | convex, Hanner polytope |
It has Schläfli symbol {4,34}, being composed of 3 5-cubes around each 4-face. It can be called a hexeract, a portmanteau of tesseract (the 4-cube) with hex for six (dimensions) in Greek. It can also be called a regular dodeca-6-tope or dodecapeton, being a 6-dimensional polytope constructed from 12 regular facets.
It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called hypercubes. The dual of a 6-cube can be called a 6-orthoplex, and is a part of the infinite family of cross-polytopes.
Applying an alternation operation, deleting alternating vertices of the 6-cube, creates another uniform polytope, called a 6-demicube, (part of an infinite family called demihypercubes), which has 12 5-demicube and 32 5-simplex facets.
This configuration matrix represents the 6-cube. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells, 4-faces and 5-faces. The diagonal numbers say how many of each element occur in the whole 6-cube. The nondiagonal numbers say how many of the column's element occur in or at the row's element.[1][2]
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a 6-cube centered at the origin and edge length 2 are
- (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1)
while the interior of the same consists of all points (x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5) with −1 < xi < 1.
There are three Coxeter groups associated with the 6-cube, one regular, with the C6 or [4,3,3,3,3] Coxeter group, and a half symmetry (D6) or [33,1,1] Coxeter group. The lowest symmetry construction is based on hyperrectangles or proprisms, cartesian products of lower dimensional hypercubes.
| Name | Coxeter | Schläfli | Symmetry | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular 6-cube | {4,3,3,3,3} | [4,3,3,3,3] | 46080 | |
| Quasiregular 6-cube | [3,3,3,31,1] | 23040 | ||
| hyperrectangle | {4,3,3,3}×{} | [4,3,3,3,2] | 7680 | |
| {4,3,3}×{4} | [4,3,3,2,4] | 3072 | ||
| {4,3}2 | [4,3,2,4,3] | 2304 | ||
| {4,3,3}×{}2 | [4,3,3,2,2] | 1536 | ||
| {4,3}×{4}×{} | [4,3,2,4,2] | 768 | ||
| {4}3 | [4,2,4,2,4] | 512 | ||
| {4,3}×{}3 | [4,3,2,2,2] | 384 | ||
| {4}2×{}2 | [4,2,4,2,2] | 256 | ||
| {4}×{}4 | [4,2,2,2,2] | 128 | ||
| {}6 | [2,2,2,2,2] | 64 |
| Coxeter plane | B6 | B5 | B4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [12] | [10] | [8] |
| Coxeter plane | Other | B3 | B2 |
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [2] | [6] | [4] |
| Coxeter plane | A5 | A3 | |
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] |
| 3D Projections | |
6-cube 6D simple rotation through 2Pi with 6D perspective projection to 3D. |
6-cube quasicrystal structure orthographically projected to 3D using the golden ratio. |
A 3D perspective projection of an hexeract undergoing a triple rotation about the X-W1, Y-W2 and Z-W3 orthogonal planes. | |
The 64 vertices of a 6-cube also represent a regular skew 4-polytope {4,3,4 | 4}. Its net can be seen as a 4×4×4 matrix of 64 cubes, a periodic subset of the cubic honeycomb, {4,3,4}, in 3-dimensions. It has 192 edges, and 192 square faces. Opposite faces fold together into a 4-cycle. Each fold direction adds 1 dimension, raising it into 6-space.
The 6-cube is 6th in a series of hypercube:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Line segment | Square | Cube | 4-cube | 5-cube | 6-cube | 7-cube | 8-cube |
This polytope is one of 63 uniform 6-polytopes generated from the B6 Coxeter plane, including the regular 6-cube or 6-orthoplex.
- Coxeter, H.S.M. Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8 p. 296, Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n>=5)
- Klitzing, Richard. "6D uniform polytopes (polypeta) o3o3o3o3o4x - ax".
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hypercube". MathWorld.
- Olshevsky, George. "Measure polytope". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
- Multi-dimensional Glossary: hypercube Garrett Jones
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform polychoron | Pentachoron | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||