Great_dodecahedron
Great dodecahedron
Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron
In geometry, the great dodecahedron is a Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol {5,5/2} and Coxeter–Dynkin diagram of ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra. It is composed of 12 pentagonal faces (six pairs of parallel pentagons), intersecting each other making a pentagrammic path, with five pentagons meeting at each vertex.
. It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra. It is composed of 12 pentagonal faces (six pairs of parallel pentagons), intersecting each other making a pentagrammic path, with five pentagons meeting at each vertex.
| Great dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron |
| Stellation core | regular dodecahedron |
| Elements | F = 12, E = 30 V = 12 (χ = -6) |
| Faces by sides | 12{5} |
| Schläfli symbol | {5,5⁄2} |
| Face configuration | V(5⁄2)5 |
| Wythoff symbol | 5⁄2 | 2 5 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532) |
| References | U35, C44, W21 |
| Properties | Regular nonconvex |
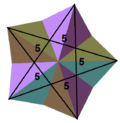 (55)/2 (Vertex figure) |
 Small stellated dodecahedron (dual polyhedron) |

The discovery of the great dodecahedron is sometimes credited to Louis Poinsot in 1810, though there is a drawing of something very similar to a great dodecahedron in the 1568 book Perspectiva Corporum Regularium by Wenzel Jamnitzer.
The great dodecahedron can be constructed analogously to the pentagram, its two-dimensional analogue, via the extension of the (n – 1)-pentagonal polytope faces of the core n-polytope (pentagons for the great dodecahedron, and line segments for the pentagram) until the figure again closes.