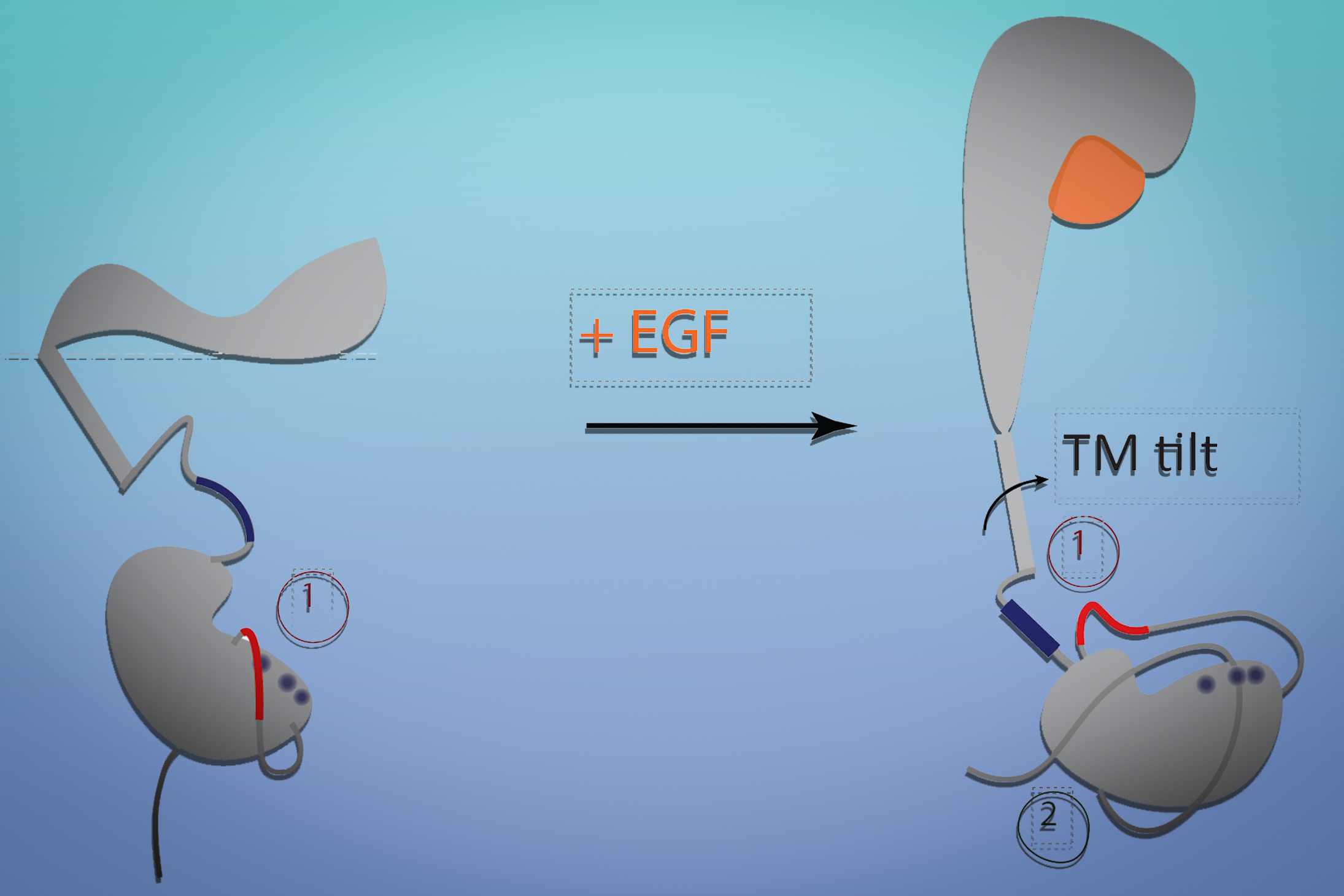
The human body has 37 trillion cells. If we can work out what they all do, the results could revolutionise healthcare
Pioneered by the Human Cell Atlas consortium, our understanding of the human body is about to be transformed – and with it, the way we treat and prevent disease
July 7, 2022 • ~24 min