Nitazenes found in 5 overdose deaths in Philly – here’s what they are and why they’re so deadly
Initially developed in the 1950s, nitazenes are a type of synthetic opioid that has reappeared in Philadelphia’s street drug supply.
Christopher P. Holstege, Professor of Emergency Medicine and Pediatrics, University of Virginia •
conversation
April 12, 2024 • ~6 min
April 12, 2024 • ~6 min
When an antibiotic fails: MIT scientists are using AI to target “sleeper” bacteria
Most antibiotics target metabolically active bacteria, but with artificial intelligence, researchers can efficiently screen compounds that are lethal to dormant microbes.
Alex Ouyang | Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health •
mit
April 8, 2024 • ~4 min
April 8, 2024 • ~4 min
A natural deception: 3 marketing myths the supplement industry wants you to swallow
‘Natural’ isn’t the same thing as healthful. You can have too much of a good thing, and taking action can be worse than doing nothing.
Katie Suleta, Doctorate in Health Sciences candidate, George Washington University •
conversation
April 5, 2024 • ~7 min
April 5, 2024 • ~7 min
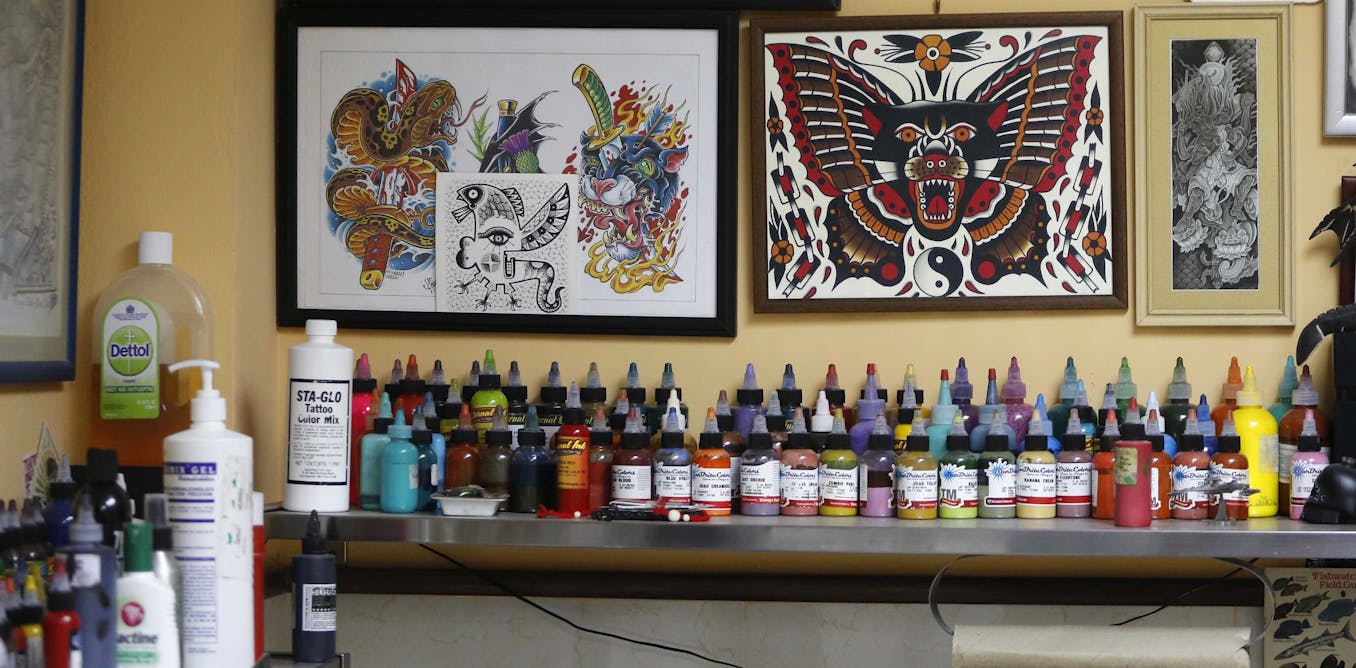
What’s in tattoo ink? My team’s chemical analysis found ingredients that aren’t on the label and could cause allergies
Some tattoo inks contain unlabeled materials that can cause allergic reactions.
John Swierk, Assistant Professor, Chemistry, Binghamton University, State University of New York •
conversation
March 22, 2024 • ~7 min
March 22, 2024 • ~7 min
AI can help predict whether a patient will respond to specific tuberculosis treatments, paving way for personalized care
People have been battling tuberculosis for thousands of years, and drug-resistant strains are on the rise. Analyzing large datasets with AI can help humanity gain a crucial edge over the disease.
Sriram Chandrasekaran, Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan •
conversation
March 20, 2024 • ~6 min
March 20, 2024 • ~6 min
/
87