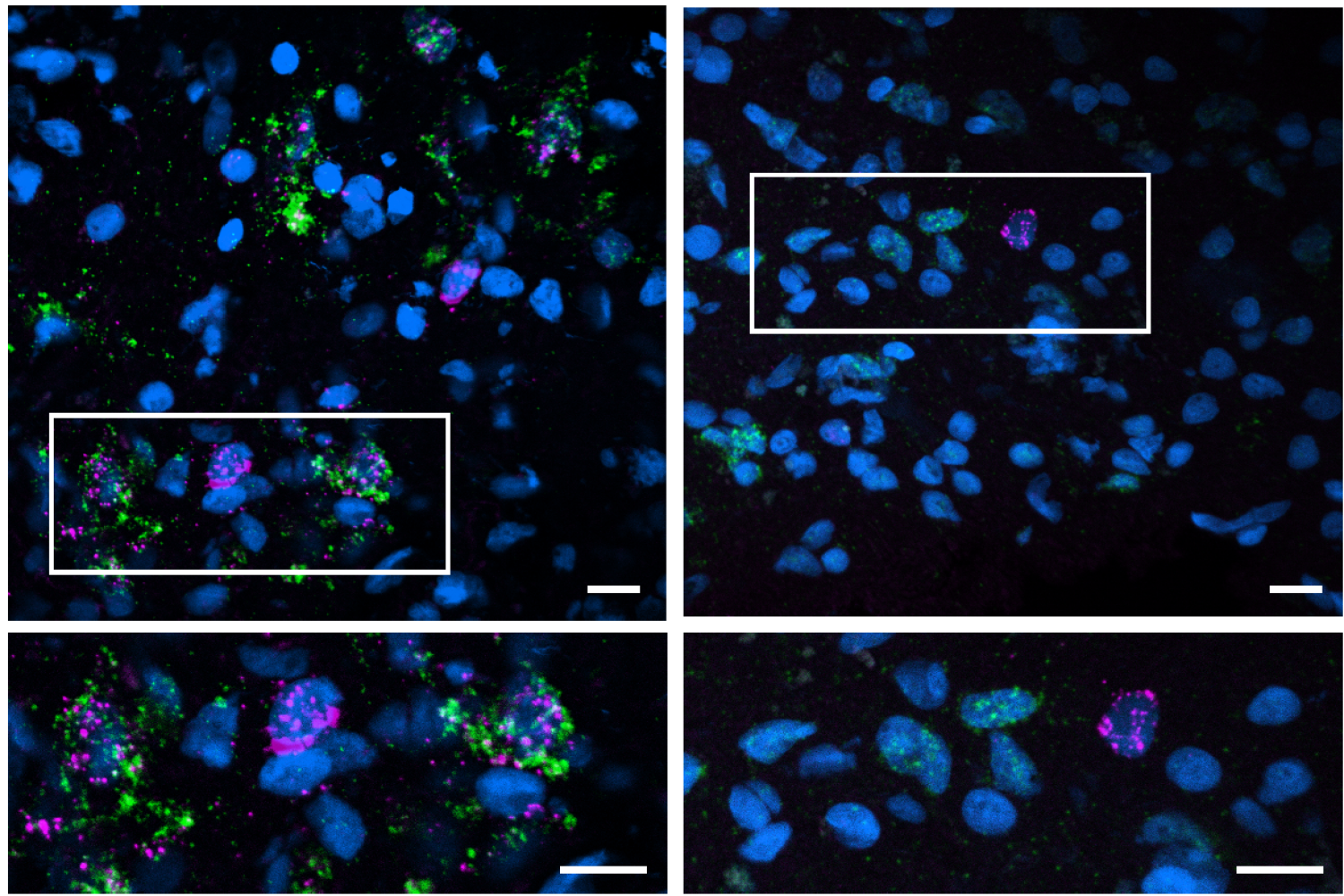
Cells have more mini ‘organs’ than researchers thought − unbound by membranes, these rogue organelles challenge biology’s fundamentals
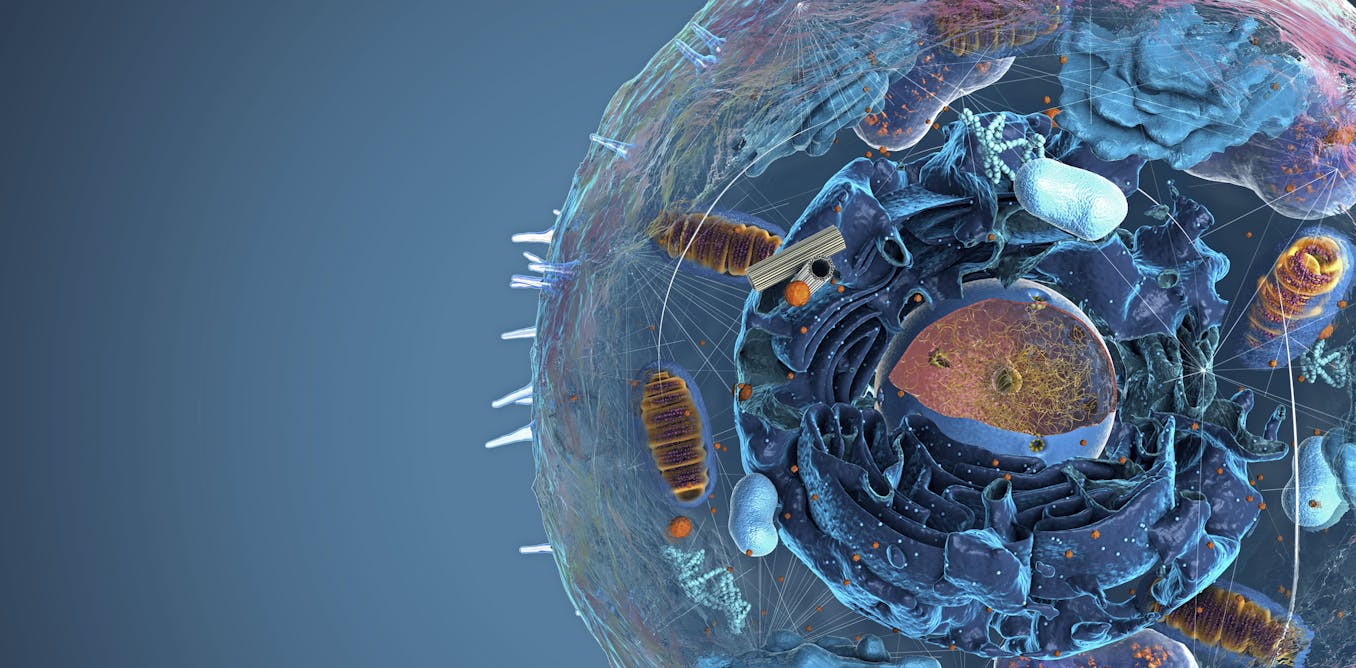
Membraneless organelles, also called biomolecular condensates, are changing how scientists think about protein chemistry, various diseases and even the origin of life.
Nov. 5, 2024 • ~8 min