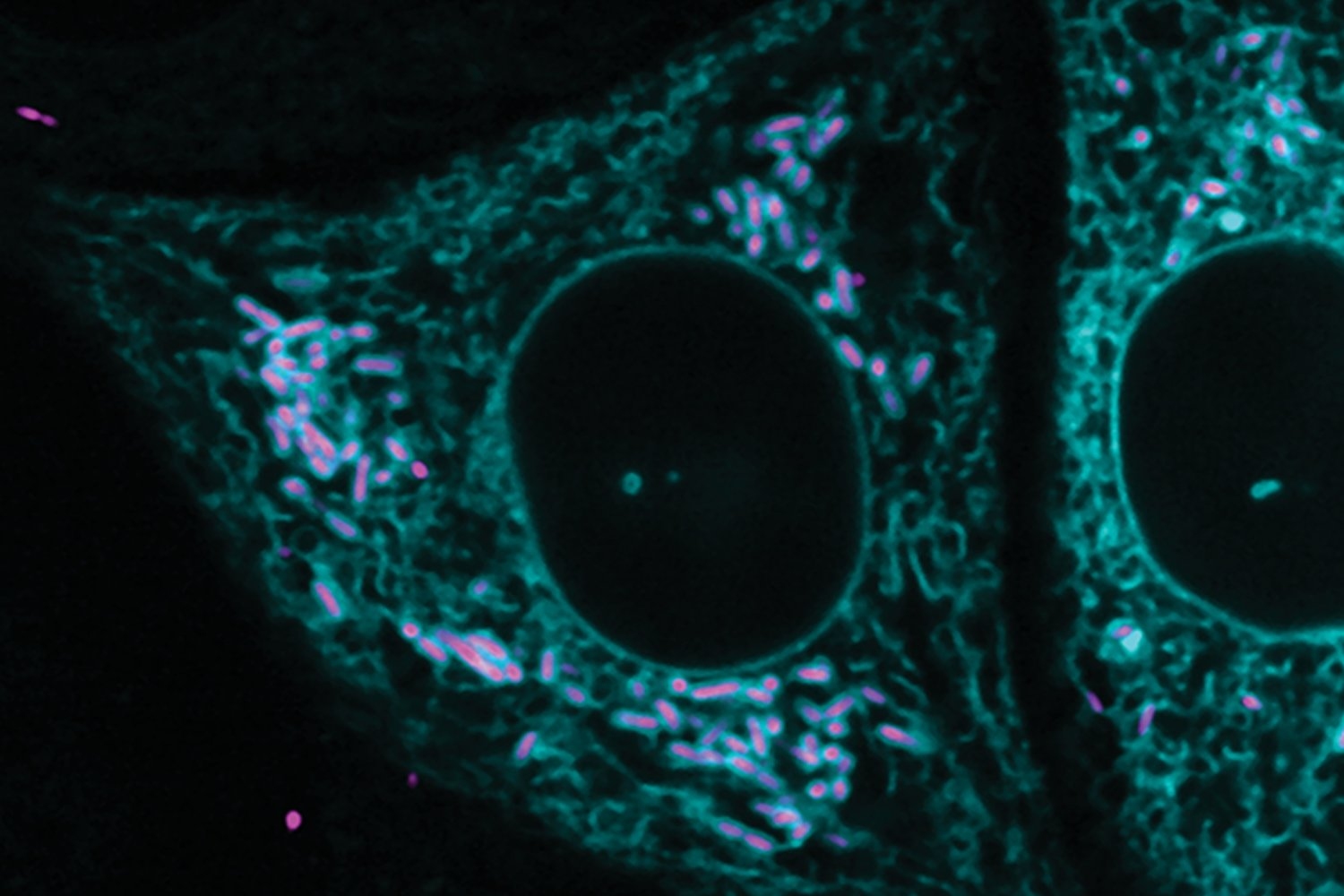
Kingdoms collide as bacteria and cells form captivating connections
Studying the pathogen R. parkeri, researchers discovered the first evidence of extensive and stable interkingdom contacts between a pathogen and a eukaryotic organelle.
Lillian Eden | Department of Biology •
mit
Jan. 24, 2025 • ~8 min
Jan. 24, 2025 • ~8 min
When an antibiotic fails: MIT scientists are using AI to target “sleeper” bacteria
Most antibiotics target metabolically active bacteria, but with artificial intelligence, researchers can efficiently screen compounds that are lethal to dormant microbes.
Alex Ouyang | Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health •
mit
April 8, 2024 • ~4 min
April 8, 2024 • ~4 min
/
16