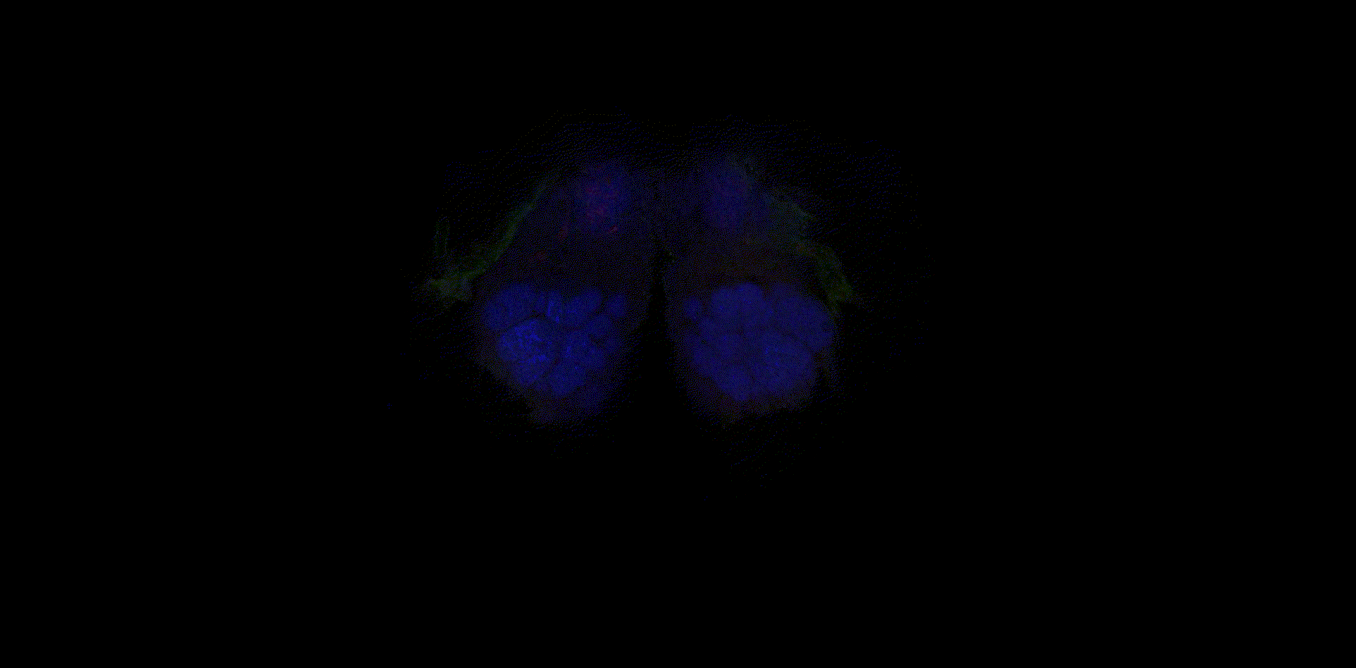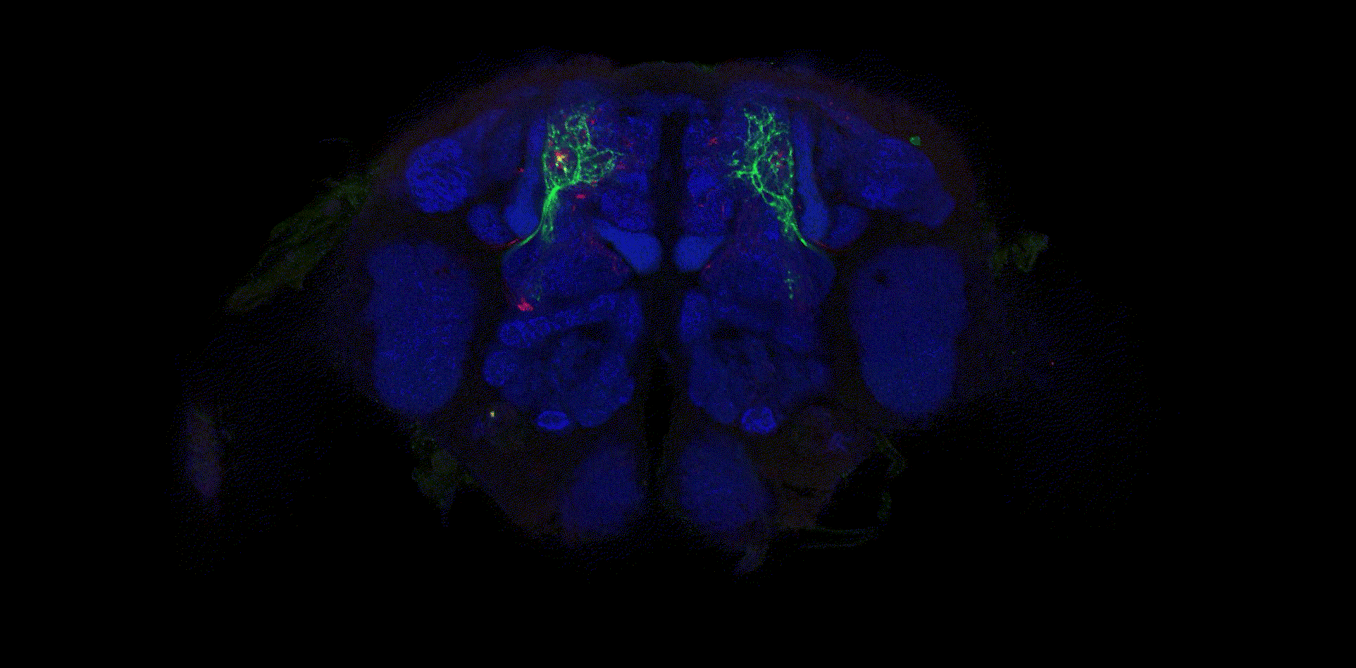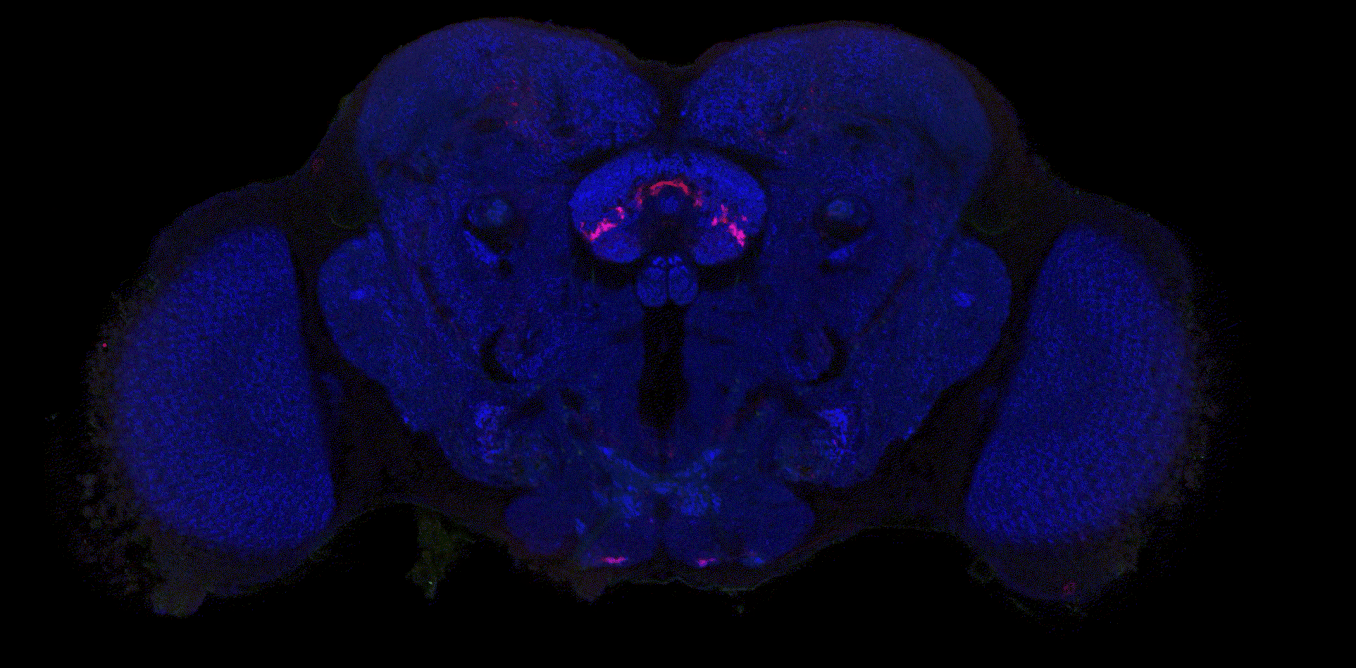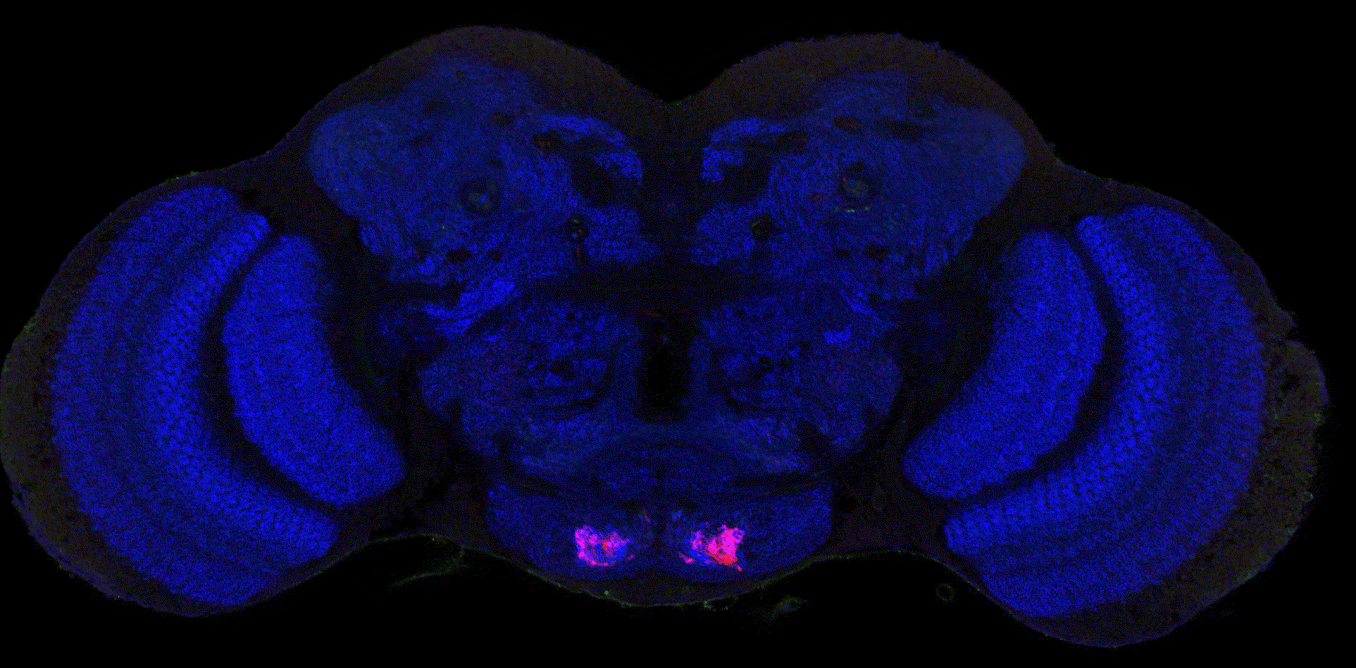
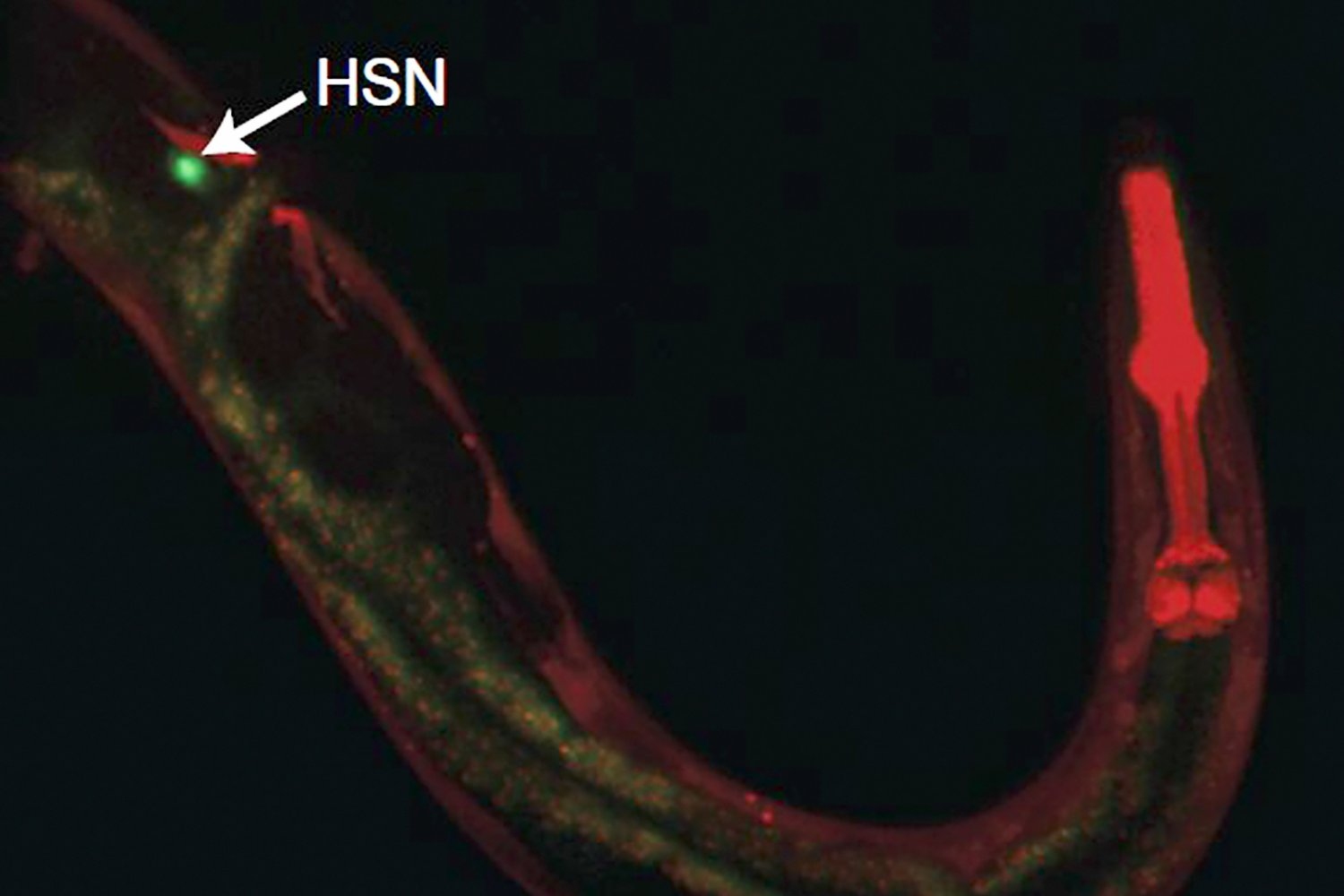
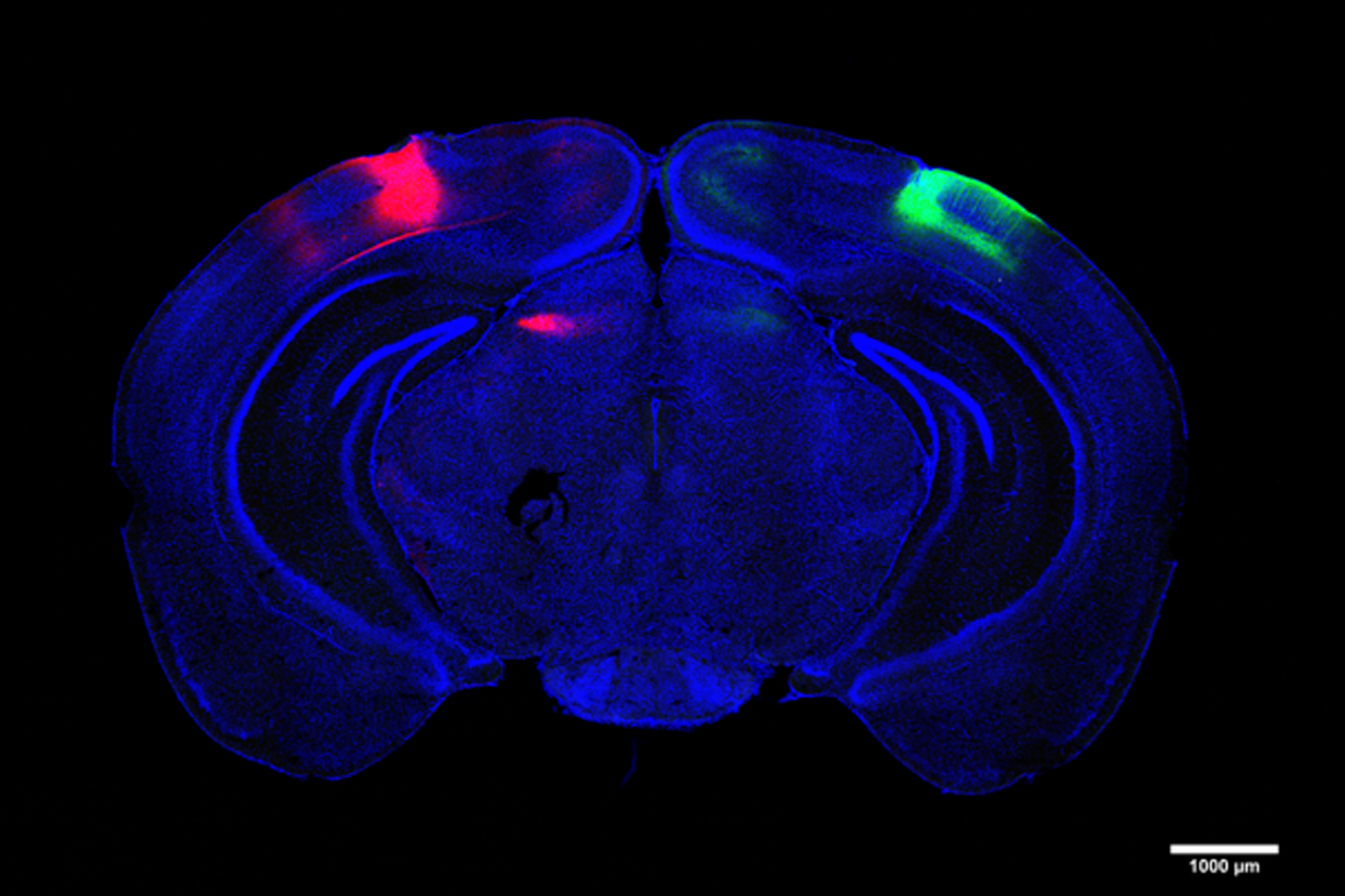
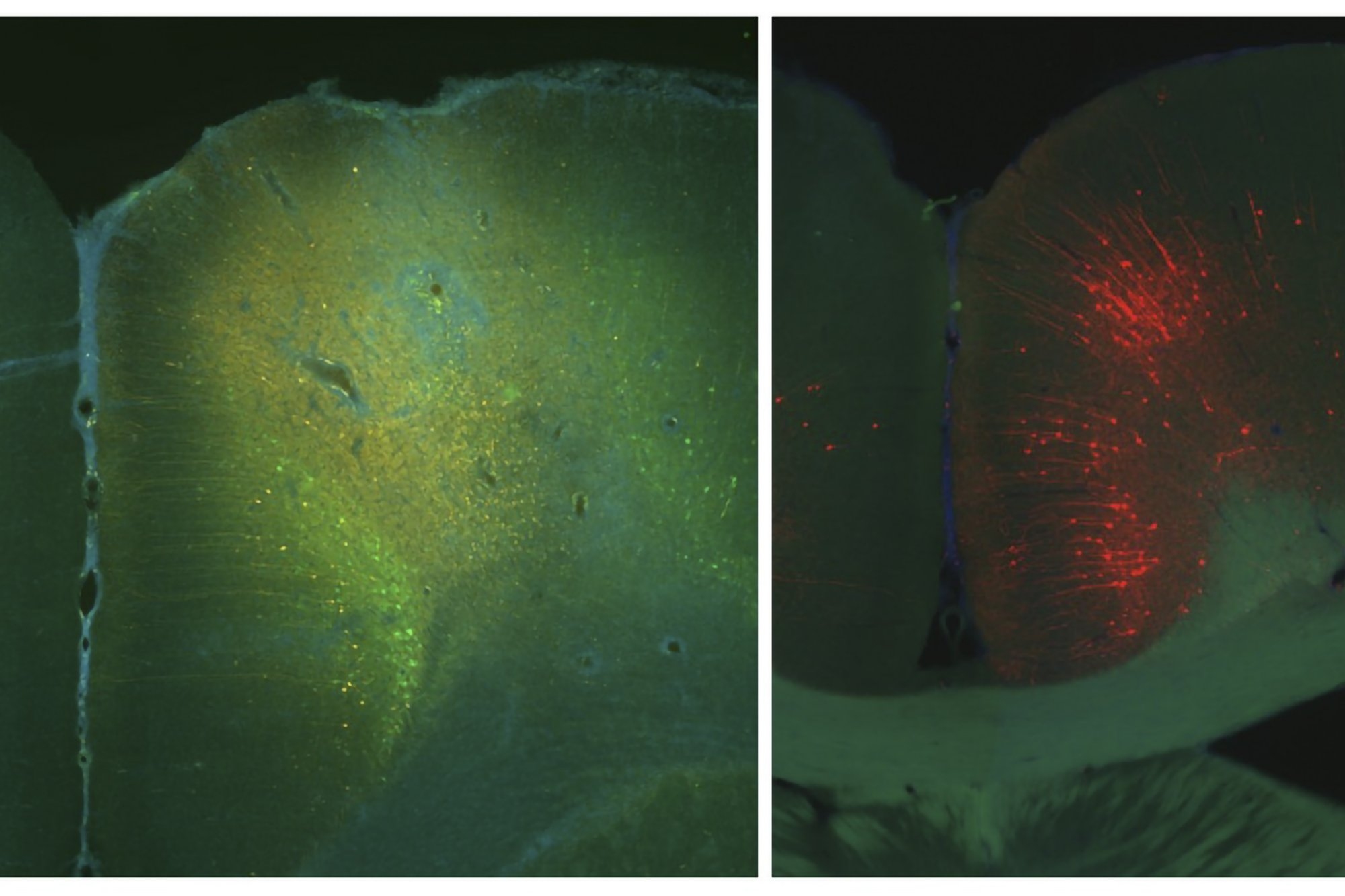
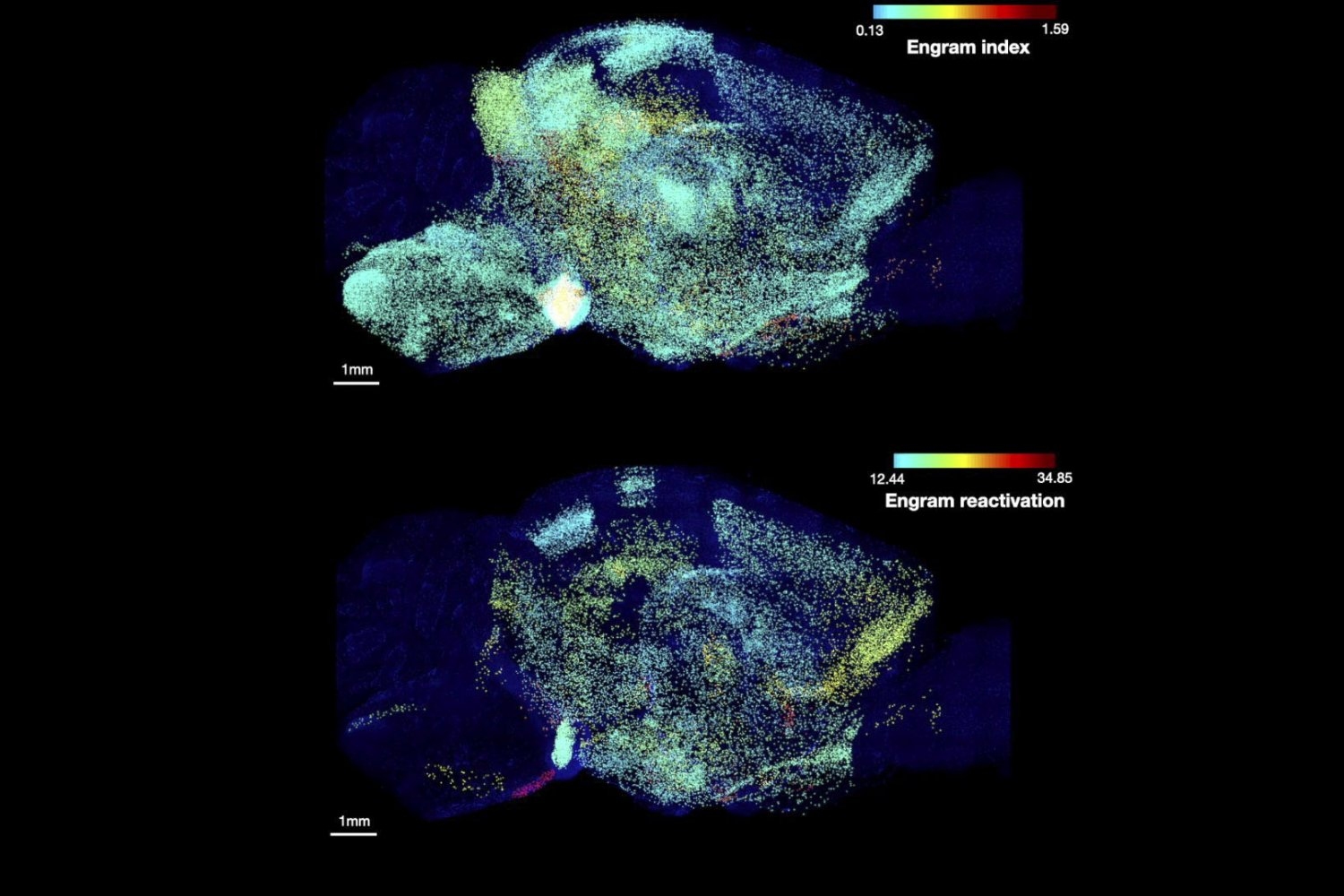
Human brains and fruit fly brains are built similarly – visualizing how helps researchers better understand how both work
Studying the human brain is difficult because of its vast and intricate network of neural connections. The fruit fly offers a simpler but similar model that researchers can more easily map.
April 15, 2024 • ~5 min