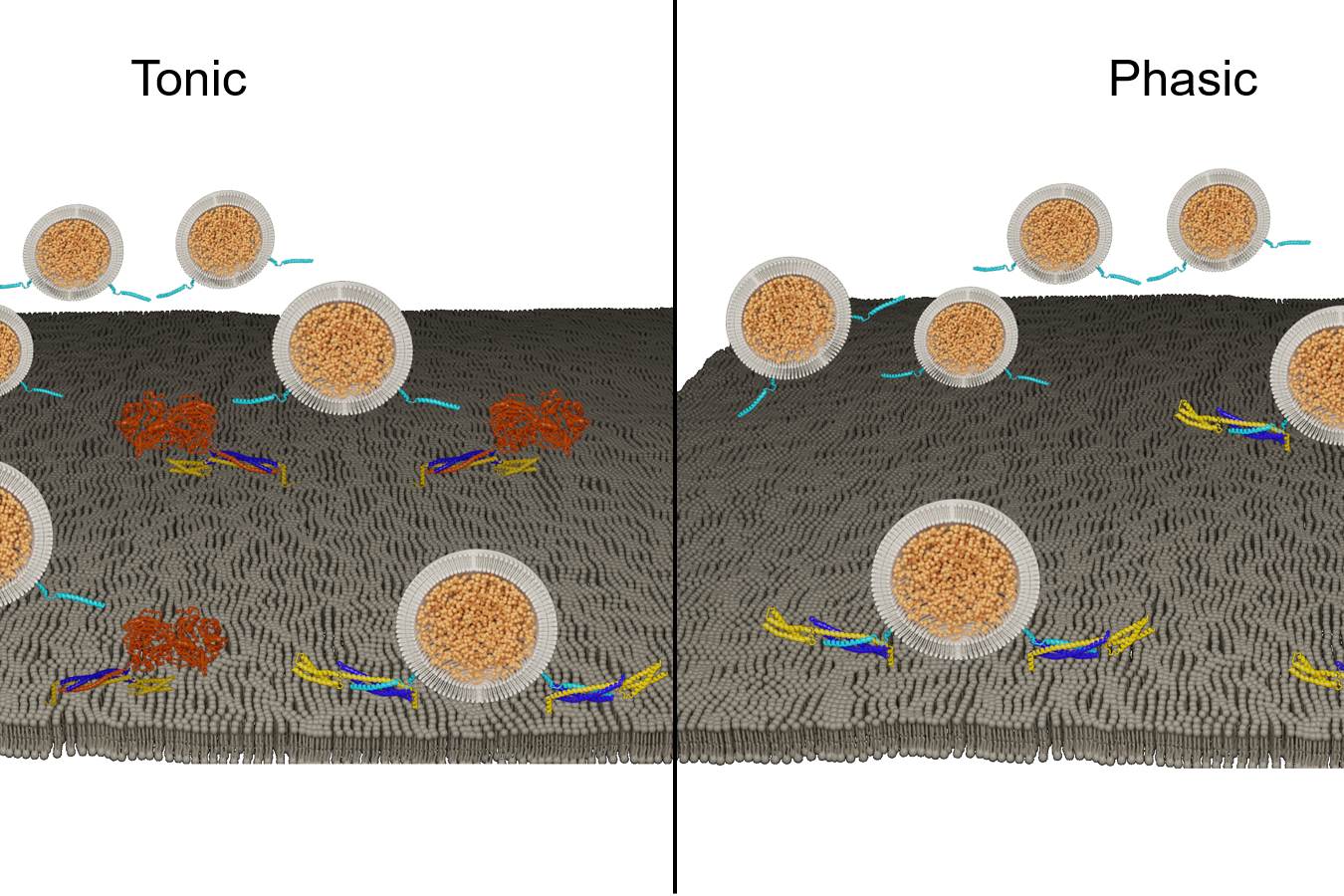
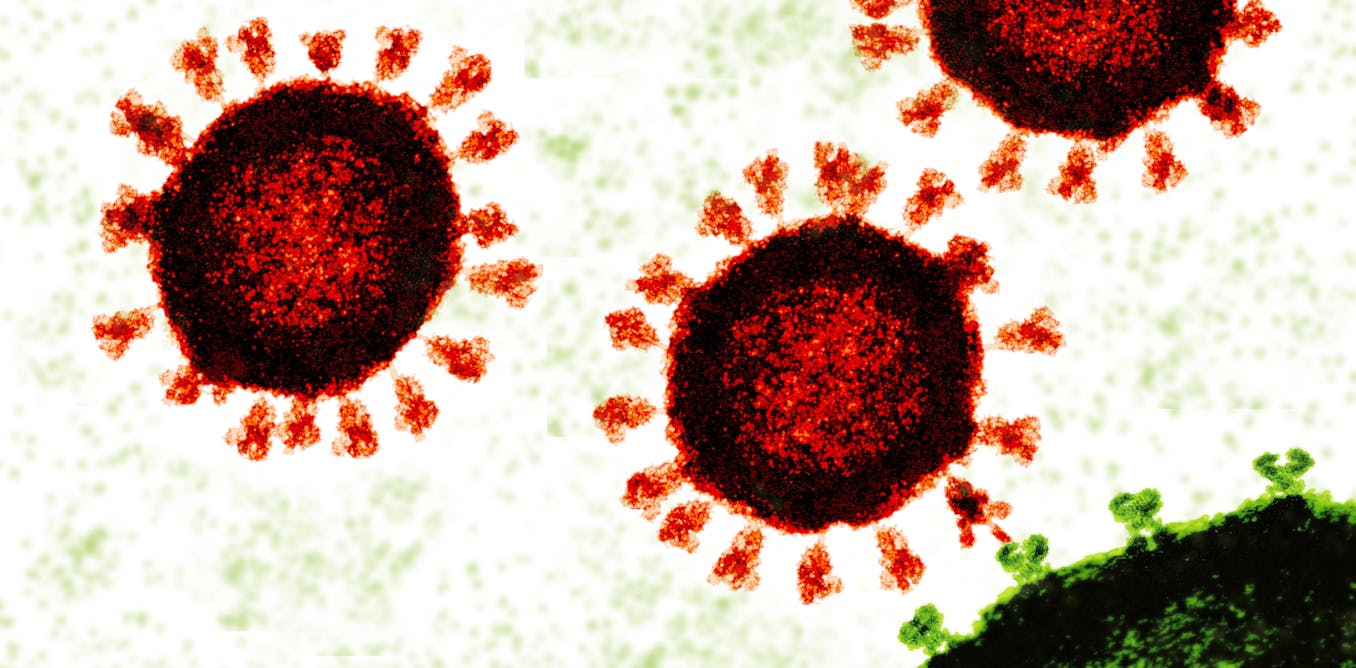
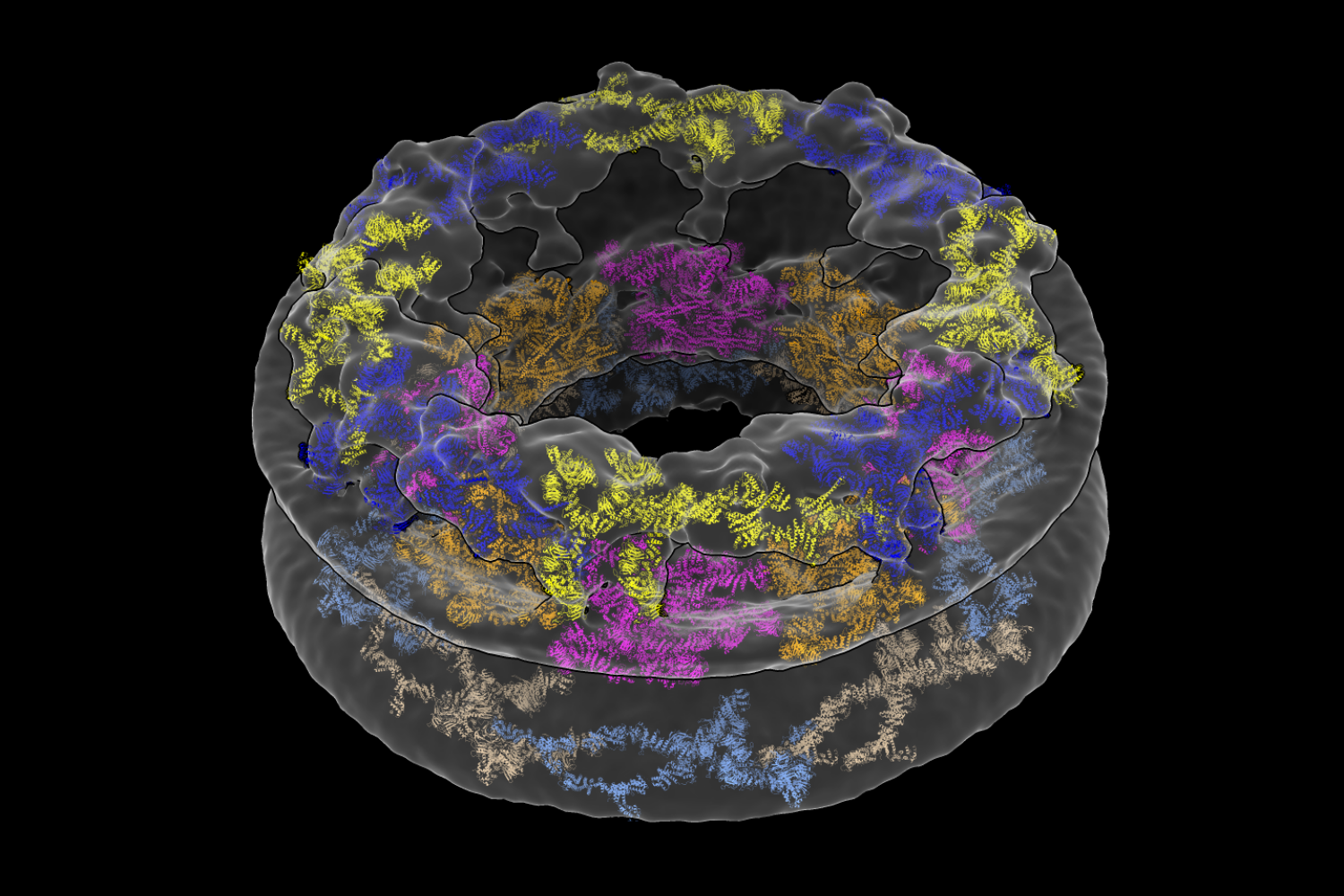
How mRNA and DNA vaccines could soon treat cancers, HIV, autoimmune disorders and genetic diseases
DNA and mRNA vaccines produce a different kind of immune response than traditional vaccines, allowing researchers to tackle some previously unsolvable problems in medicine.
Jan. 24, 2022 • ~9 min