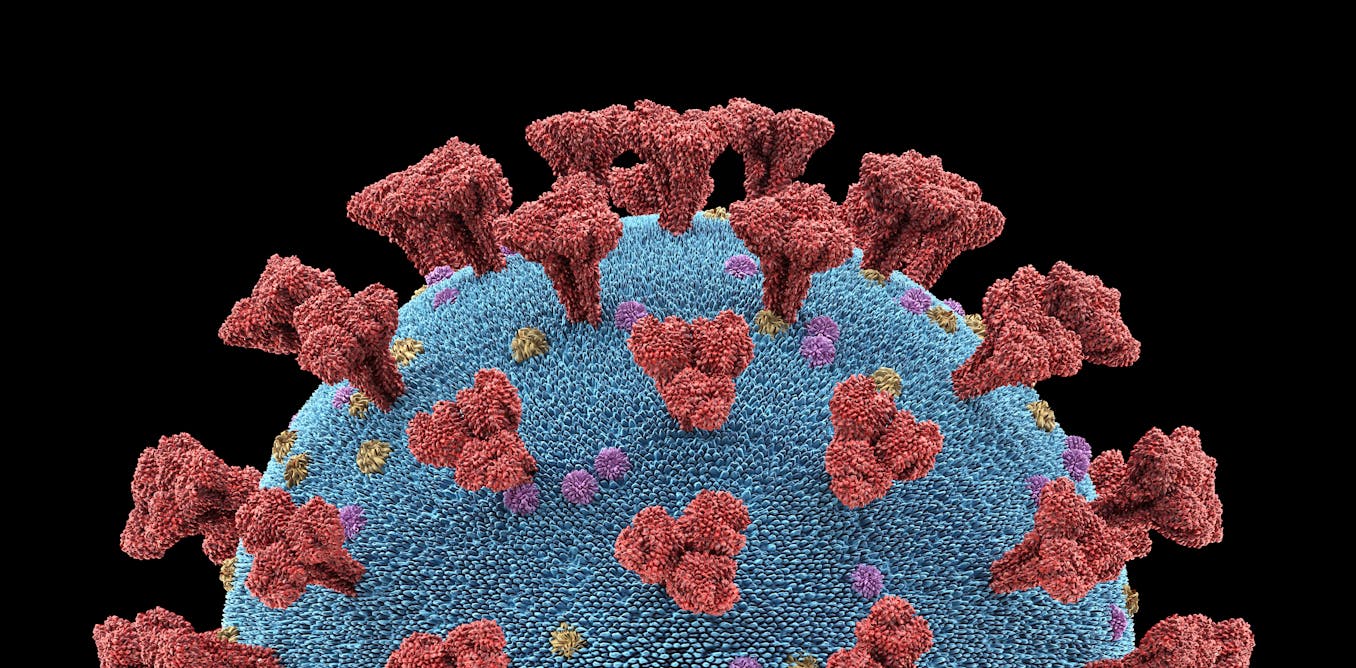
A second pathway into cells for SARS-CoV-2: New understanding of the neuropilin-1 protein could speed vaccine research
Scientists in the UK and Germany discovered a new doorway that the COVID-19 virus uses to infect human cells. This reveals new therapeutic possibilities for blocking the virus.
Oct. 23, 2020 • ~10 min