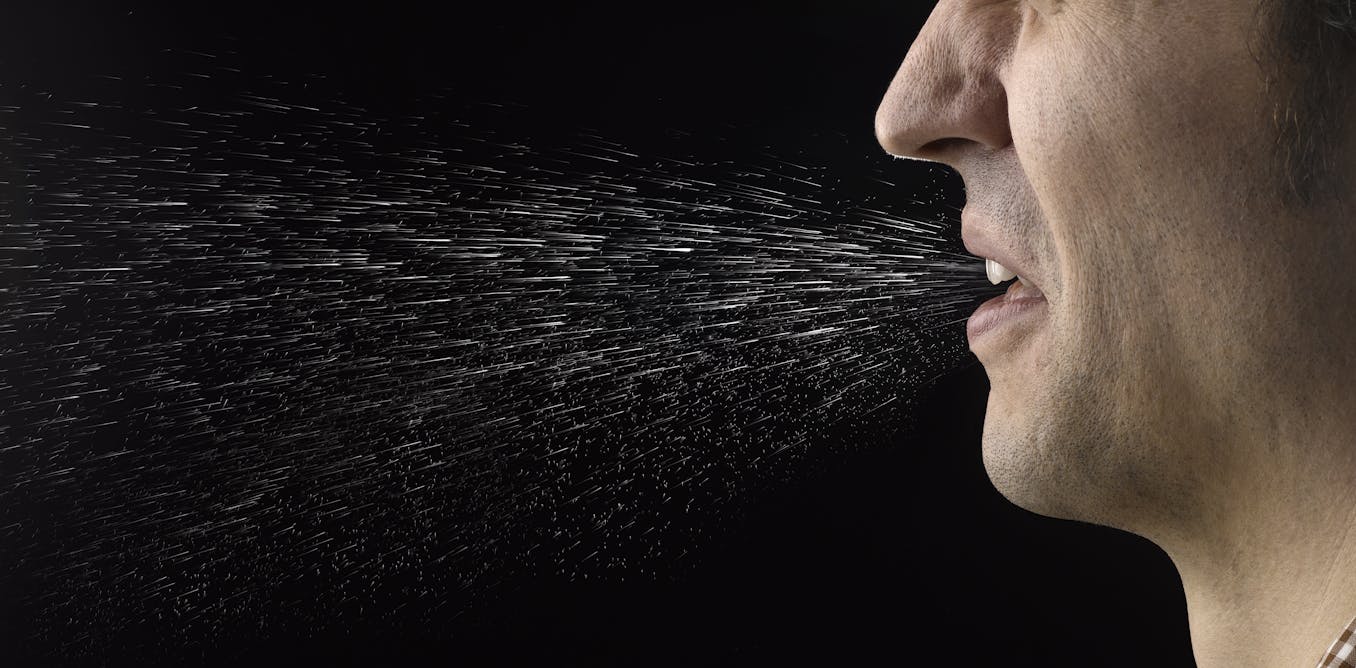
Cloth masks do protect the wearer – breathing in less coronavirus means you get less sick
In places where everyone wears a mask, cases of COVID-19 seem to be less severe. Evidence from labs and outbreaks suggests that masks protect not only others, but the person wearing the mask, too.
Aug. 19, 2020 • ~8 min
The COVID-19 virus can spread through the air – here's what it'll take to detect the airborne particles
Miniaturized laboratory equipment is making it easier to identify airborne pathogens in the field, but there's still work ahead to be able to instantly determine if a room is safe or contaminated.
Aug. 14, 2020 • ~9 min
Rapid screening tests that prioritize speed over accuracy could be key to ending the coronavirus pandemic
Testing large numbers of people regularly would reduce the spread of the coronavirus in the US. Laboratory testing is slow and expensive, but rapid screening tests could be the answer.
Aug. 14, 2020 • ~9 min
Does coronavirus linger in the body? What we know about how viruses in general hang on in the brain and testicles
Some viruses can hide out in the body and reemerge at later times. Which viruses do this, and can the new coronavirus do this too?
July 31, 2020 • ~9 min
Coronavirus numbers confusing you? Here's how to make sense of them
There's more to the numbers than what you see on TV.
July 21, 2020 • ~6 min
How deadly is the coronavirus? The true fatality rate is tricky to find, but researchers are getting closer
The percentage of people who die from a coronavirus infection is an important number for public health experts to know. Recent estimates now put it at 0.26%, far lower than initially thought.
July 15, 2020 • ~9 min
Aerosols are a bigger coronavirus threat than WHO guidelines suggest – here's what you need to know
More than 200 scientists wrote to the WHO, warning about aerosol transmission of the coronavirus. The WHO has since acknowledged the evidence but hasn't change its advice yet.
July 9, 2020 • ~9 min
/
18