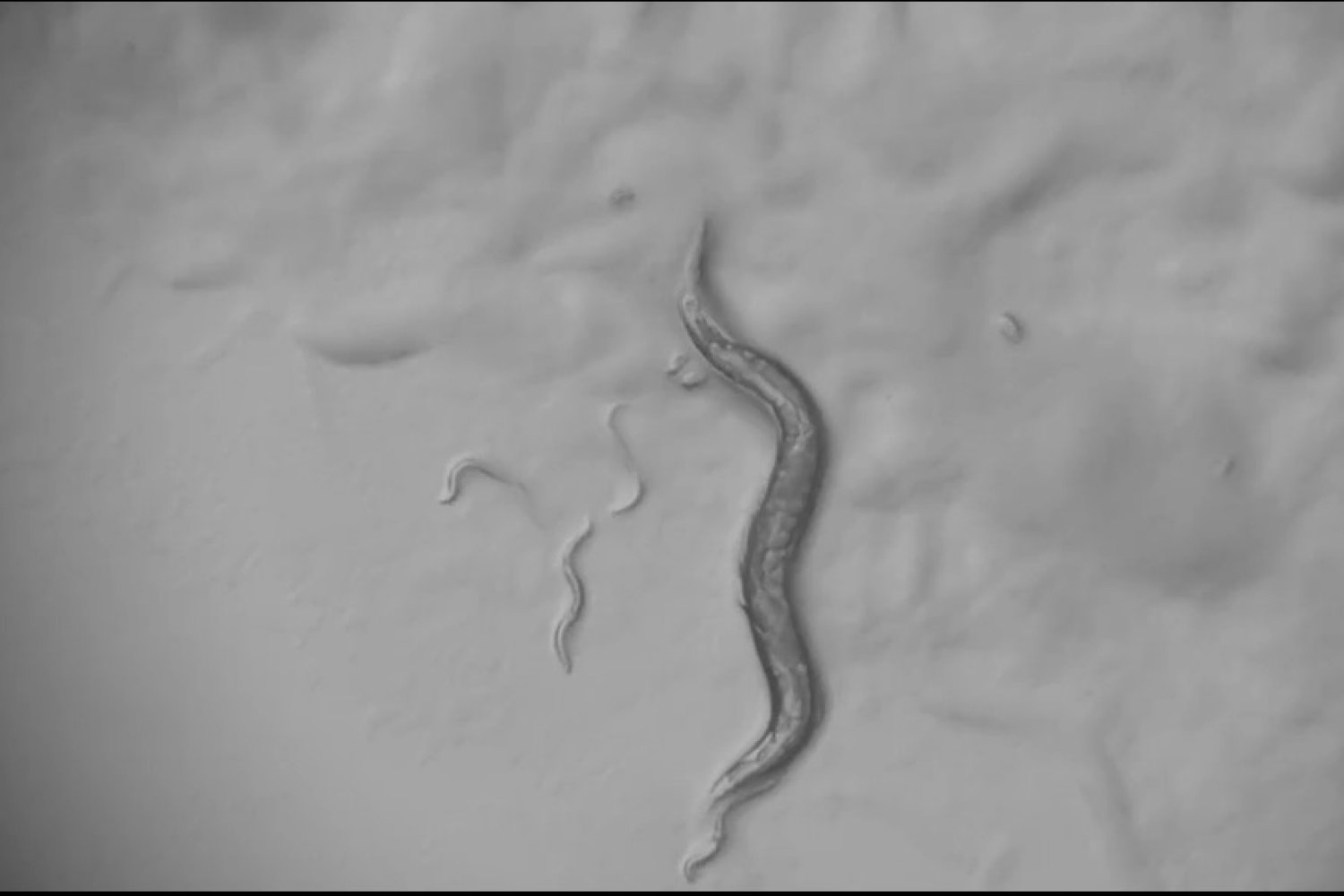
Response to infection highlights the nervous system’s surprising degrees of flexibility
Upon infection, the C. elegans worm reshuffles the roles of brain cells and flips the functions of some of the chemicals it uses to regulate behavior.
David Orenstein | The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory •
mit
April 29, 2025 • ~8 min
April 29, 2025 • ~8 min
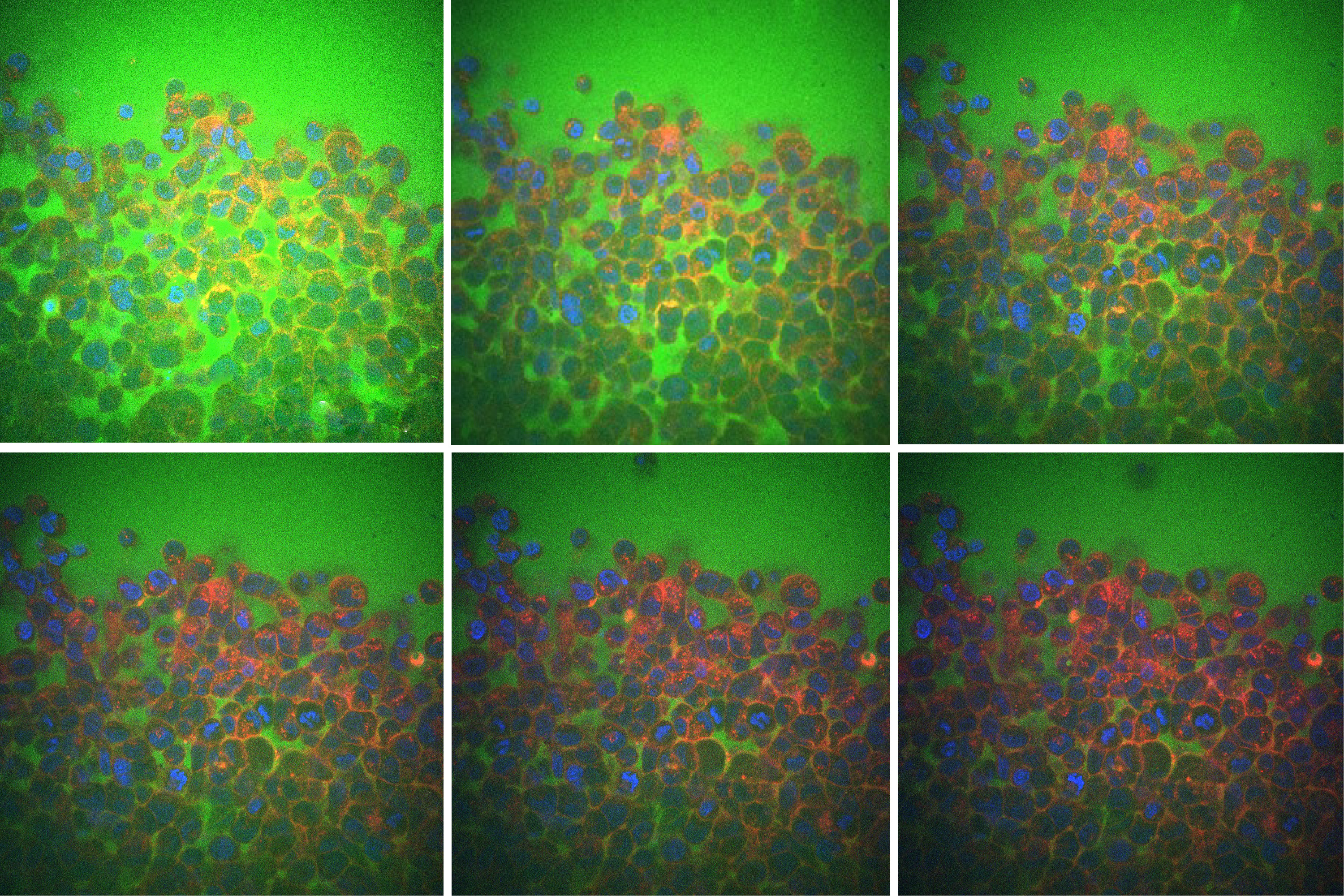
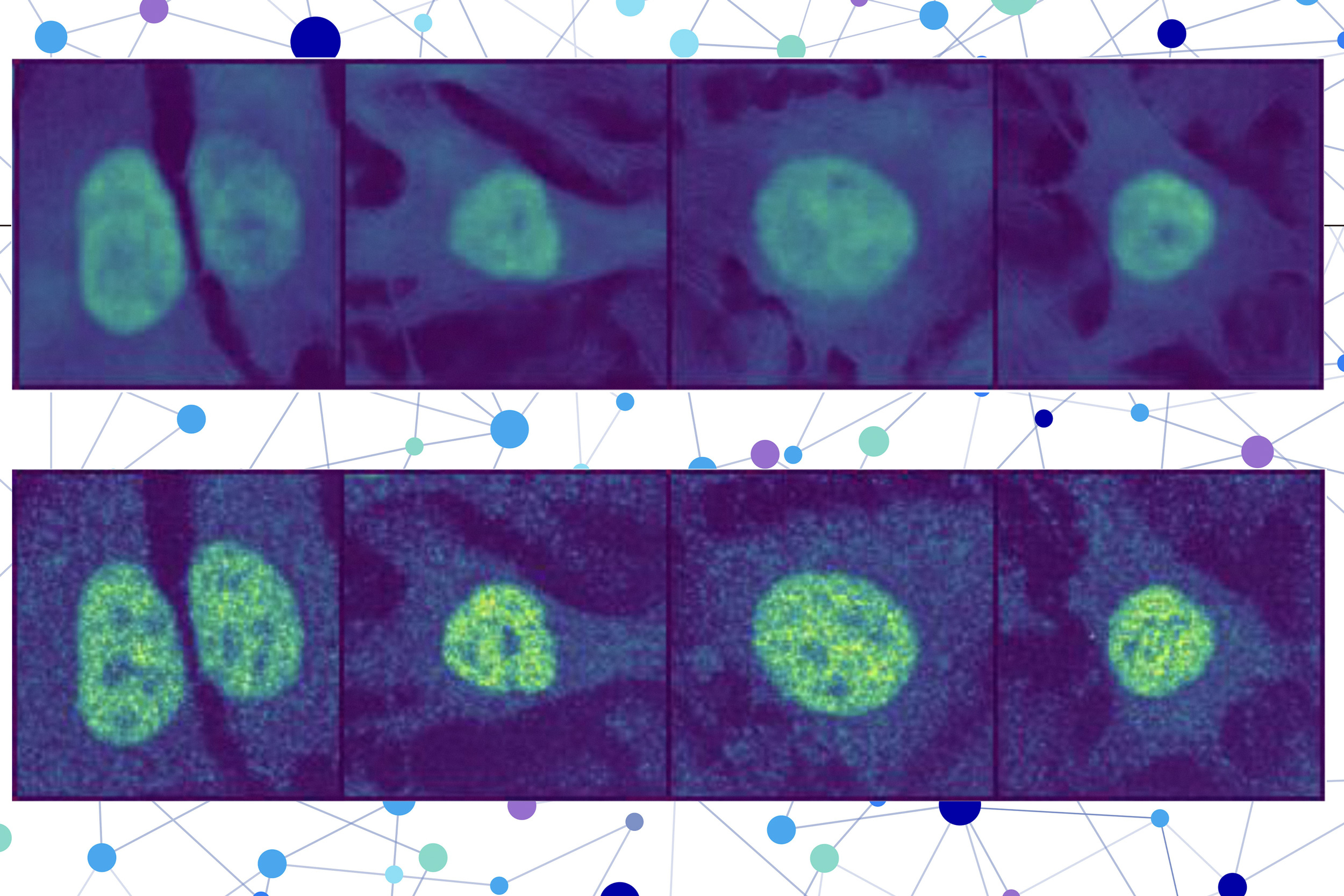
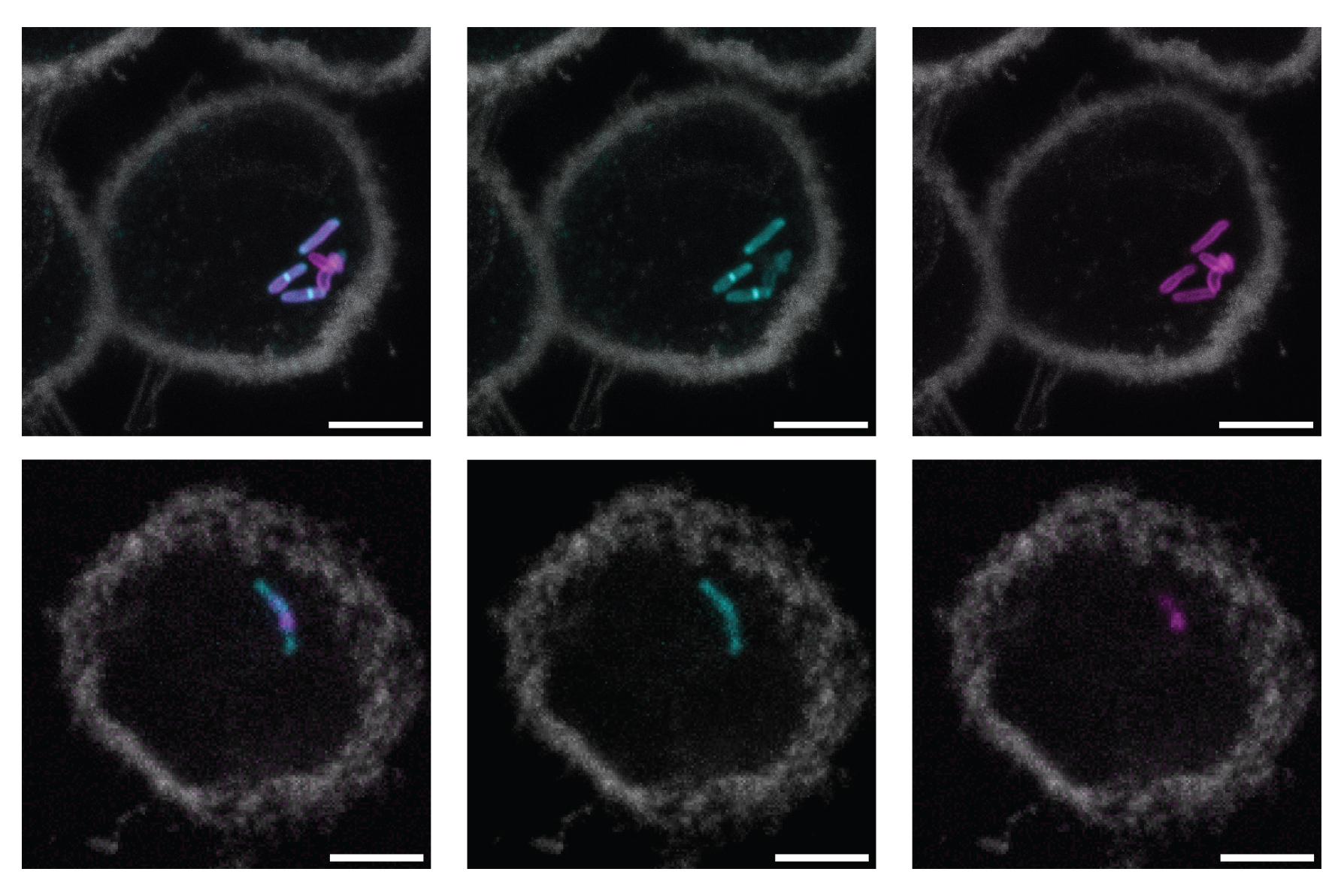
A brief history of expansion microscopy
Since an MIT team introduced expansion microscopy in 2015, the technique has powered the science behind kidney disease, plant seeds, the microbiome, Alzheimer’s, viruses, and more.
Jennifer Michalowski | McGovern Institute for Brain Research •
mit
April 23, 2025 • ~13 min
April 23, 2025 • ~13 min
/
25