Study connects neural gene expression differences to functional distinctions
Researchers compared a pair of superficially similar motor neurons in fruit flies to examine how their differing use of the same genome produced distinctions in form and function.
David Orenstein | The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory •
mit
Aug. 25, 2023 • ~8 min
Aug. 25, 2023 • ~8 min
It takes three to tango: transcription factors bind DNA, protein, and RNA
Whitehead Institute researchers find many transcription factors bind RNA, which fine-tunes their regulation of gene expression, suggesting new therapeutic opportunities.
Greta Friar | Whitehead Institute •
mit
July 17, 2023 • ~7 min
July 17, 2023 • ~7 min
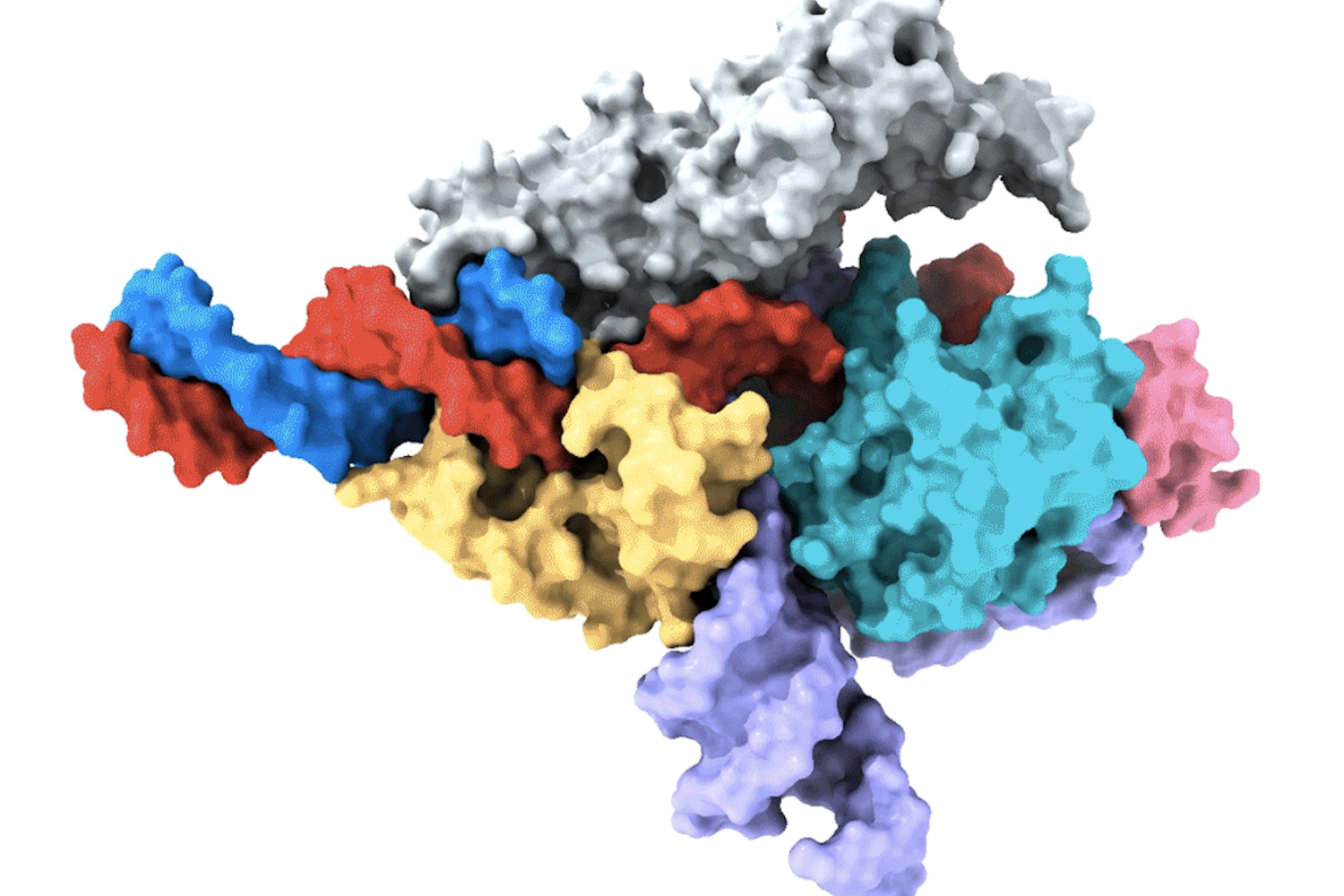
Researchers uncover a new CRISPR-like system in animals that can edit the human genome
The first RNA-guided DNA-cutting enzyme found in eukaryotes, Fanzor could one day be harnessed to edit DNA more precisely than CRISPR/Cas systems.
Leah Eisenstadt | McGovern Institute for Brain Research | Broad Institute •
mit
June 28, 2023 • ~7 min
June 28, 2023 • ~7 min
/
23